Page 164 - IJB-10-6
P. 164
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D bioprinting technology for brain tumor
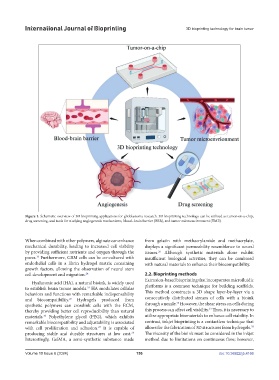
Figure 1. Schematic overview of 3D bioprinting applications for glioblastoma research. 3D bioprinting technology can be utilized as tumor-on-a-chip,
drug screening, and tools for studying angiogenesis mechanisms, blood–brain barrier (BBB), and tumor microenvironment (TME).
When combined with other polymers, alginate can enhance from gelatin with methacrylamide and methacrylate,
mechanical durability, leading to increased cell viability displays a significant permeability resemblance to neural
by providing sufficient nutrients and oxygen through the tissues. Although synthetic materials alone exhibit
26
pores. Furthermore, GBM cells can be co-cultured with insufficient biological activities, they can be combined
19
endothelial cells in a fibrin hydrogel matrix containing with natural materials to enhance their biocompatibility.
growth factors, allowing the observation of neural stem
cell development and migration. 24 2.2. Bioprinting methods
Extrusion-based bioprinting that incorporates microfluidic
Hyaluronic acid (HA), a natural bioink, is widely used
to establish brain tumor models. HA modulates cellular platforms is a common technique for building scaffolds.
24
behaviors and functions with remarkable indispensability This method constructs a 3D shape layer-by-layer via a
and biocompatibility. Hydrogels produced from consecutively distributed stream of cells with a bioink
25
50
synthetic polymers can crosslink cells with the ECM, through a nozzle. However, the shear stress on cells during
23
thereby providing better cell reproducibility than natural this process can affect cell viability. Thus, it is necessary to
materials. Polyethylene glycol (PEG), which exhibits utilize appropriate biomaterials to enhance cell viability. In
26
remarkable biocompatibility and adjustability, is associated contrast, inkjet bioprinting is a contactless technique that
with cell proliferation and adhesion. It is capable of allows for the fabrication of 3D structures from hydrogels.
28
27
producing stable and durable structures at low cost. The viscosity of the bioink must be considered in the inkjet
28
Interestingly, GelMA, a semi-synthetic substance made method due to limitations on continuous flow; however,
Volume 10 Issue 6 (2024) 156 doi: 10.36922/ijb.4166