Page 512 - IJB-10-6
P. 512
International Journal of Bioprinting Redefined collagen inks in cartilage printing
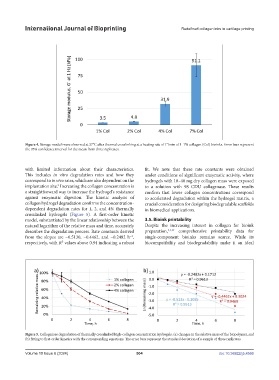
Figure 4. Storage moduli were observed at 37°C after thermal crosslinking at a heating rate of 1°/min of 1–7% collagen (Col) bioinks. Error bars represent
the 95% confidence interval for the mean from three replicates.
with limited information about their characteristics. fit. We note that these rate constants were obtained
This includes in vitro degradation rates and how they under conditions of significant enzymatic activity, where
correspond to in vivo rates, which are also dependent on the hydrogels with 10–40 mg dry collagen mass were exposed
implantation site. Increasing the collagen concentration is to a solution with 98 CDU collagenase. These results
3
a straightforward way to increase the hydrogel’s resistance confirm that lower collagen concentrations correspond
against enzymatic digestion. The kinetic analysis of to accelerated degradation within the hydrogel matrix, a
collagen hydrogel degradation confirms the concentration- crucial consideration for designing biodegradable scaffolds
dependent degradation rates for 1, 2, and 4% thermally in biomedical applications.
crosslinked hydrogels (Figure 5). A first-order kinetic
model, substantiated by the linear relationship between the 3.5. Bioink printability
natural logarithm of the relative mass and time, accurately Despite the increasing interest in collagen for bioink
describes the degradation process. Rate constants derived preparation, 3,5,49 comprehensive printability data for
from the slopes are −0.5130, −0.4462, and −0.2482 h ¹, single-component bioinks remains scarce. While its
–
respectively, with R² values above 0.94 indicating a robust biocompatibility and biodegradability make it an ideal
Figure 5. Collagenase degradation of thermally crosslinked high-collagen concentration hydrogels: (a) changes in the relative mass of the biopolymer, and
(b) fitting to first-order kinetics with the corresponding equations. The error bars represent the standard deviation of a sample of three replicates.
Volume 10 Issue 6 (2024) 504 doi: 10.36922/ijb.4566