Page 29 - IJB-7-1
P. 29
Attarilar, et al.
beam is patterned by the utilization of another device defined layer thickness, the powder bed is lowered, and
such as Digital Micromirror Device™. In the two-photon the fresh layer of powder is prepared after the completion
approach, the photopolymerization process is implemented of previous layers. This method was repeated several
at the intersecting point of two laser beams . times to complete the fabrication [19,20] .
[16]
2.2. Powder-bed fusion (1) SLM method
In powder-bed 3DP techniques, a thermal source is Being one of the most popular prototyping methods, the
utilized to selectively melt or fuse the substances (wax, SLM method uses high power-density laser to fuse metal
[22]
metal, nylon, polymer, plastic, ceramic, composite) or metallic alloy powders to produce AlSi10Mg parts ,
which are held in a tray and the melt or fused materials martensitic high strength steel , and Al–Scalloy . The
[24]
[23]
are then sequentially printed in a layer-by-layer manner. production of 3D part by SLM involves a series of steps
Several examples of the printing methods following the from digital design data preparation to the removal of
power-bed 3D printing include EBM, SLS, polymer laser the completed part from the building platform. First, to
sintering, direct metal laser sintering and SLM . generate the slice data of each layer for laser scanning,
[18]
The basic of laser powder-bed fusion is shown in SLA (STL) files must be produced by software such as
Figure 6A. A laser beam scans the target location of the Materialise Magics. Then, the CAD data are uploaded
powder bed with specified speed and energy to convert to the SLM machine. The building procedure starts with
the powder fusion into solid form, under full melting SLS laying the first thin layer of metal powder on a tray. Soon
(SLM) or partial melting SLS condition. According to the after the powder is laid, a laser beam with a high energy-
A B C
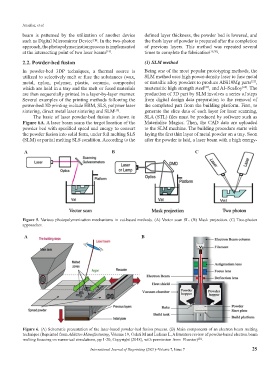
Figure 5. Various photopolymerization mechanisms in vat-based methods. (A) Vector scan SL. (B) Mask projection. (C) Two-photon
approaches.
A B
Figure 6. (A) Schematic presentation of the laser-based powder-bed fusion process. (B) Main components of an electron beam melting
technique (Reprinted from Additive Manufacturing, Volume 19, Galati M and Luliano L, A literature review of powder-based electron beam
melting focusing on numerical simulations, pp 1-20, Copyright (2018), with permission from Elsevier) .
[21]
International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 7 25