Page 32 - IJB-7-1
P. 32
3D Printing Technologies in Metallic Implants
Figure 10. Schematic illustration of material jetting or multijet
modelling (Reproduced by permission of The Royal Society
of Chemistry) .
[44]
be used in two distinctive ways along with material Figure 11. Schematic representation of laminated object
melting (precise extrusion deposition , precise extrusion manufacturing (Reprinted from Laser Additive
[45]
manufacturing , multiphase jet solidification , and Manufacturing, Hagedorn Y, Laser additive manufacturing of
[46]
[47]
fused deposition modeling ) and without material ceramic components: Materials, processes and mechanisms,
[48]
melting (direct-write assembly , solvent-based extrusion pp. 163-180, Copyright (2017), with permission from
[49]
[57]
free-forming , 3D bioplotting, robocasting , pressure- Elsevier) .
[50]
[51]
assisted microsyringe , and low temperature deposition
[52]
manufacturing) . FDM is the most well-known among production price, (iii) lower fragility or higher durability,
[53]
these versatile material extrusion techniques. In FDM, the (iv) a wide range of materials with versatile mechanical
material (usually a thermoplastic or composite) is extruded and chemical properties can be used in LOM, and (v) no
by special nozzle systems which consist of, for instance, post-processing is required. Unfortunately, the z-direction
heated and digitally controllable nozzles that can move in all accuracy of LOM products is low.
three directions. After the heating or melting procedure, the
material or substance that flows through the nozzle equipped 2.7. Directed energy deposition (DED)
with a temperature control system will rapidly solidify upon In DED methods, a focused energy source like laser
its first contact with the air. After the deposition of the first and electron beam and plasma arc is utilized to melt the
layer, the stage is lowered to continue and complete the material, and the melted substance is deposited in the wire
layer-by-layer formation of the 3D object [39,44] . or in powder form through a nozzle. This method uses both
2.6. Sheet lamination features of material extrusion and power bed fusion AM
processes. Unlike DED, the powder-bed fusion method
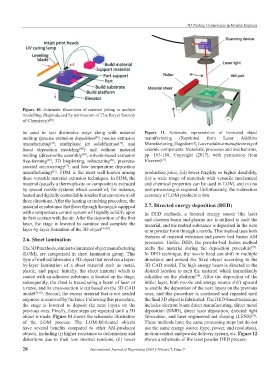
The 3DP methods, similar to laminated object manufacturing melts the material during the deposition procedure .
[57]
(LOM), are categorized in sheet lamination group. This In DED technique, the nozzle head can shift in multiple
type of method fabricates a 3D object that involves a layer- directions and around the fixed object according to the
by-layer lamination of a sheet material such as metal, 3D CAD model. The high-energy beam is directed to the
plastic, and paper. Initially, the sheet material which is desired location to melt the material which immediately
coated with an adhesive substance is located on the stage; solidifies on the platform . After the deposition of the
[58]
subsequently, the sheet is traced using a beam of laser or initial layer, both nozzle and energy source shift upward
a razor, and its cross-section is cut based on the 3D CAD to enable the deposition of the next layers on the previous
model [54,55] . Second, the excess material that is not needed ones, and this procedure is continued and repeated until
anymore is removed by the laser. Following this procedure, the final 3D object is fabricated. The DED-based technique
the stage is lowered to deposit the next layers on the includes electron beam direct manufacturing, direct metal
previous ones. Finally, these steps are repeated until a 3D deposition (DMD), direct laser deposition, directed light
object is made. Figure 11 shows the schematic illustration fabrication, and laser engineered net shaping (LENS) .
[58]
of the LOM process. The LOM-fabricated objects These methods have the same processing steps but do not
have several benefits compared to other AM-produced use the same energy source (type, power, and resolution),
objects, including (i) higher resistance to deformation and motion-control and powder delivery system, etc. Figure 12
distortions due to their low internal tensions, (ii) lower shows a schematic of the laser powder DED process.
28 International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 7