Page 33 - IJB-7-1
P. 33
Attarilar, et al.
particle pores are usually produced due to insufficient
melting of metal powders, and afterward incomplete
bonding but the fabrication of these inter-particle pores is
totally undesirable. On the other hand, the pre-designed
pores are in a regular arrangement and are particularly
used for triggering osteoinduction, reduction of elastic
modulus, and weight of implant [79-82] . The word “pore” in
this review refers to the pre-designed version.
Pore size is among the crucial parameters which
control the osteogenesis, migration of various cells,
and supplement of nutrients and thus, the optimal pore
size should be used in implant applications [83,84] . The
favorable pore size for cell seeding should be in the range
from 100 to 400 μm. It was reported that above this size
range, cell seeding would become extremely difficult, the
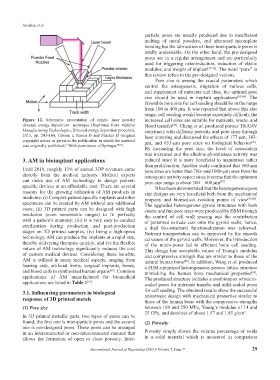
Figure 12. Schematic presentation of simple laser powder increased cell sizes are suitable for nutrients, waste, and
directed energy deposition technique (Reprinted from Additive blood transfer . Cheng et al. produced porous Ti6Al4V
[85]
Manufacturing Technologies, Directed energy deposition processes, constructs with different porosity and pore sizes through
2015, pp. 245-168, Gibson I, Rosen D and Stucker B (original laser sintering and discussed the effects of 177-μm, 383-
copyright notice as given in the publication in which the material μm, and 653-μm pore sizes on biological behavior .
[86]
was originally published) “With permission of Springer” .
[59]
By increasing the pore size, the level of osteocalcin
was increased and the alkaline phosphatase activity was
3. AM in bioimplant applications reduced since it is more beneficial to maturation rather
than proliferation. Another study confirmed that 500-μm
Until 2019, roughly 13% of annual 3DP revenues come pore sizes are better than 700- and 1000-μm ones from the
directly from the medical industry. Medical experts osteogenic activity aspect since it seems that the optimum
can make use of AM technology to design patient- pore size range is about 300 – 600 μm .
[87]
specific devices at an affordable cost. There are several It has been demonstrated that the heterogeneous pore
reasons for the growing utilization of AM products in size designs are very beneficial both from the mechanical
medicine: (i) Complex patient-specific implants and other property and biomedical reaction points of view [85,88] .
specimens can be created by AM without any additional The upgraded heterogenous gyroid structures with both
costs; (ii) 3D printed parts can be designed with high coarse and fine pore sizes were produced by EBM through
resolution (even nanometric ranges) to fit perfectly the control of cell wall spacing and the contribution
with a patient’s anatomy; (iii) it is very easy to conduct of patterned extrude cuts onto the gyroid walls; hence,
sterilization during production and post-production a dual bio-structural functionalization was achieved.
stages on 3D printed samples; (iv) being a high-speed Nutrient transportation can be improved by the smooth
technology, AM can produce the implants at a rapid rate, curvature of the gyroid walls. Moreover, the introduction
thereby delivering therapies quickly; and (v) the flexible of the micro-pores led to efficient bone cell seeding.
nature of AM technology significantly reduces the cost This design has acceptable values of Young’s modulus
of custom medical devices. Considering these benefits, and compressive strength that are similar to those of the
AM is utilized in many medical aspects, ranging from natural human bone . In addition, Wang et al. produced
[88]
hearing aids, artificial limbs, surgical implants, bones, a FEM-optimized heterogeneous porous lattice structure
and blood cells to synthesized human organs . Common mimicking the human bone mechanical properties .
[60]
[85]
applications of AM manufactured for biomedical The produced structure includes a combination of micro-
applications are listed in Table 1 . scaled pores for nutrients transfer and milli-scaled pores
[61]
3.1. Influencing parameters in biological for cell seeding. The obtained results show the successful
response of 3D printed metals anisotropic design with mechanical properties similar to
those of the human bone with the compressive strengths
(1) Pore size between 169 and 250 MPa, Young’s modulus of 14 and
3
In 3D printed metallic parts, two types of pores can be 25 GPa, and densities of about 1.57 and 1.85 g/cm .
found; the first one is inter-particle pores and the second (2) Porosity
one is pre-designed pores. These pores can be arranged
in an interconnected or non-interconnected manner that Porosity simply shows the volume percentage of voids
allows the formation of open or close porosity. Inter- in a solid material which is measured in comparison
International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 7 29