Page 28 - IJB-7-1
P. 28
3D Printing Technologies in Metallic Implants
Figure 3. An overview of the most important additive manufacturing technologies.
(CDLP), and bio-plotters use vat photopolymerization
technology . In the photopolymerization technology,
[13]
the primarily used materials are liquid, radiation-curable
resins, or photopolymers such as polyimides, elastomers,
pure polymer resin, composite resins, supramolecular
polymers, graphene, and ceramic slurry + resins. Mostly,
UV wavelength and some light systems can be used for
radiation of photopolymers. Radiation on photopolymer
materials leads to a chemical reaction, known as
photopolymerization, that solidifies the materials.
Photopolymers were first used in 1960s and later applied Figure 4. A schematic diagram of the stereolithography vat-based
in glossy coatings of papers and cardboards, dentistry, etc. technique.
In the middle of the 1980s, Charles Hull fabricated a 3D
solid part by laser scanning over a UV-curable material mechanisms are used in vat-based photopolymerization
and cured one layer over a previous layer, representing methods, including vector scan SL, mask projection,
the very first step toward SLA technology . In this and two-photon approach (Figure 5). Among different
[16]
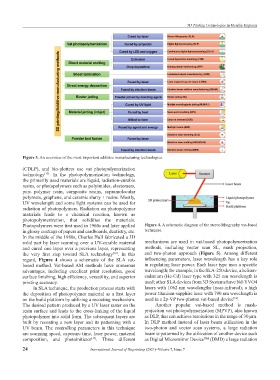
regard, Figure 4 shows a schematic of the SLA vat- influencing parameters, laser wavelength has a key role
based method. Vat-based AM methods have numerous in regulating laser power. Each laser type uses a specific
advantages, including excellent print resolution, good wavelength; for example, in the SLA-250 device, a helium-
surface finishing, high efficiency, versatility, and superior cadmium (He-Cd) laser type with 325 nm wavelength is
printing accuracy. used; other SLA devices from 3D Systems have Nd-YVO4
In SLA technique, the production process starts with lasers with 1062 nm wavelengths (near-infrared); a high
the deposition of photopolymer material as a first layer power titanium-sapphire laser with 790 nm wavelength is
[16]
on the build platform by utilizing a recoating mechanism. used in a 2p-VP two-photon vat-based device .
The desired pattern produced by a UV laser raster on the Another popular vat-based method is mask-
resin surface and leads to the cross-linking of the liquid projection vat photopolymerization (MPVP), also known
photopolymer into solid form. The subsequent layers are as DLP, that can achieve resolutions in the range of 30 μm.
built by recoating a new layer and its patterning with a In DLP method instead of laser beam utilization in the
UV beam. The controlling parameters in this technique two-photon and vector scan systems, a large radiation
are scanning speed, exposure time, laser power, material beam is patterned by the utilization of another device such
composition, and photoinitiator . Three different as Digital Micromirror Device™ (DMD) a large radiation
[17]
24 International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 7