Page 101 - IJB-7-2
P. 101
Qian, et al.
without Zn-MS was smooth, while many particles were others [28-31] . In general, cells cannot adhere on the surface
observed on the fractured surface of the composite of synthesized-polymers directly because the integrins
scaffold with addition of Zn-MS. Moreover, the number on the surface of cell membrane can only interact
of particles increased with increasing amount of Zn-MS. with specific amino acid sequences of proteins in the
The EDS results confirmed that the components of the extracellular matrix . Good hydrophilicity is beneficial
[32]
particles were Zn, Si, and O elements, indicating the to absorb nutrients and proteins in the body fluids, thus
particles were Zn-MS. It was noted that the particles significantly promoting cell adhesion .
[33]
distributed evenly on the PLLA matrix when the adding The mechanical properties also collectively
amount of Zn-MS was below 6 wt.%. However, when represent an important evaluation index for bone repairing
the amount of Zn-MS was 6 wt.%, obvious aggregation materials. The proper mechanical properties of implants
appeared on the fractured surface of the composite are able to reduce the appearance of fracture remarkably
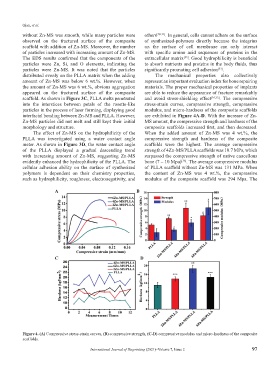
scaffold. As shown in Figure 3C, PLLA melts penetrated and avoid stress-shielding effect [34,35] . The compressive
into the interstices between petals of the rosette-like stress-strain curves, compressive strength, compressive
particles in the process of laser forming, displaying good modulus, and micro-hardness of the composite scaffolds
interfacial bonding between Zn-MS and PLLA. However, are exhibited in Figure 4A-D. With the increase of Zn-
Zn-MS particles did not melt and still kept their initial MS amount, the compressive strength and hardness of the
morphology and structure. composite scaffolds increased first, and then decreased.
The effect of Zn-MS on the hydrophilicity of the When the added amount of Zn-MS was 4 wt.%, the
PLLA was investigated using a water contact angle compressive strength and hardness of the composite
meter. As shown in Figure 3D, the water contact angle scaffolds were the highest. The average compressive
of the PLLA displayed a gradual descending trend strength of 4Zn-MS/PLLA scaffolds was 10.7 MPa, which
with increasing amount of Zn-MS, suggesting Zn-MS surpassed the compressive strength of native cancellous
evidently enhanced the hydrophilicity of the PLLA. The bone (7 – 10 Mpa) . The average compressive modulus
[36]
cellular adhesion ability on the surface of synthesized of PLLA scaffold without Zn-MS was 131 MPa. When
polymers is dependent on their chemistry properties, the content of Zn-MS was 4 wt.%, the compressive
such as hydrophilicity, roughness, electronegativity, and modulus of the composite scaffold was 294 Mpa. The
A B
C D
Figure 4. (A) Compressive stress-strain curves, (B) compressive strength, (C-D) compressive modulus and micro-hardness of the composite
scaffolds.
International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 2 97