Page 104 - IJB-7-2
P. 104
3D Printed and Ion Controllable Release
A B
C D
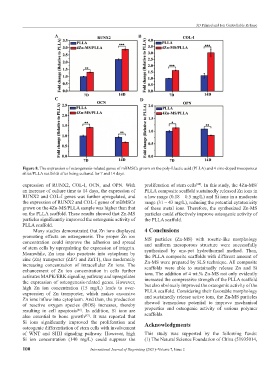
Figure 8. The expression of osteogenesis-related genes of mBMSCs grown on the poly-Llactic acid (PLLA) and 4 zinc-doped mesoporous
silica/PLLA scaffolds after being cultured for 7 and 14 days.
expression of RUNX2, COL-I, OCN, and OPN. With proliferation of stem cells . In this study, the 4Zn-MS/
[48]
an increase of culture time to 14 days, the expression of PLLA composite scaffold sustainedly released Zn ions in
RUNX2 and COL-I genes was further upregulated, and a low range (0.18 – 0.5 mg/L) and Si ions in a moderate
the expression of RUNX2 and COL-I genes of mBMSCs range (31 – 43 mg/L), reducing the potential cytotoxicity
grown on the 4Zn-MS/PLLA sample was higher than that of these metal ions. Therefore, the synthesized Zn-MS
on the PLLA scaffold. These results showed that Zn-MS particles could effectively improve osteogenic activity of
particles significantly improved the osteogenic activity of the PLLA scaffold.
PLLA scaffold.
Many studies demonstrated that Zn ions displayed 4 Conclusions
promoting effects on osteogenesis. The proper Zn ion MS particles (Zn-MS) with rosette-like morphology
concentration could improve the adhesion and spread and uniform mesoporous structure were successfully
of stem cells by upregulating the expression of integrin. synthesized by one-pot hydrothermal method. Then,
Meanwhile, Zn ions also penetrate into cytoplasm by the PLLA composite scaffolds with different amount of
zinc (Zn) transporter (ZIP1 and ZnT1), thus moderately Zn-MS were prepared by SLS technique. All composite
increasing concentration of intracellular Zn ions. The scaffolds were able to sustainedly release Zn and Si
enhancement of Zn ion concentration in cells further ions. The addition of 4 wt.% Zn-MS not only evidently
activates MAPK/ERK signaling pathway and upregulates increased the compressive strength of the PLLA scaffold
the expression of osteogenesis-related genes. However,
high Zn ion concentration (15 mg/L) leads to over- but also obviously improved the osteogenic activity of the
expression of Zn transporter, which makes excessive PLLA scaffold. Considering their favorable morphology
Zn ions inflow into cytoplasm. And then, the production and sustainedly release active ions, the Zn-MS particles
of reactive oxygen species (ROS) increases, thereby showed tremendous potential to improve mechanical
resulting in cell apoptosis . In addition, Si ions are properties and osteogenic activity of various polymer
[46]
also essential to bone growth . It was reported that scaffolds.
[47]
Si ions significantly improved the proliferation and Acknowledgments
osteogenic differentiation of stem cells with involvement
of WNT and SHH signaling pathway. However, high This study was supported by the following funds:
Si ion concentration (140 mg/L) could suppress the (1) The Natural Science Foundation of China (51935014,
100 International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 2