Page 110 - IJB-7-2
P. 110
Technique of Thyroid Cartilage Scaffold Support Formation
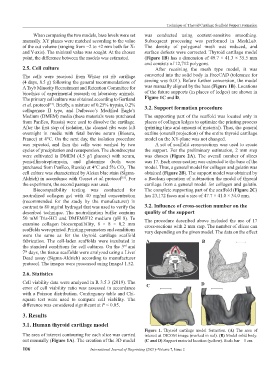
When comparing the two models, base levels were set was conducted using context-sensitive smoothing.
manually. XY planes were matched according to the value Subsequent processing was performed in MeshLab.
of the cut volume (ranging from −2 to +2 mm both for X- The density of polygonal mesh was reduced, and
and Y-axis). The minimal value was sought. At the chosen surface defects were corrected. Thyroid cartilage model
point, the difference between the models was estimated. (Figure 1B) has a dimension of 49.7 × 41.3 × 35.5 mm
and consists of 12,712 polygons.
2.5. Cell culture After receiving the mesh type model, it was
The cells were received from Wistar rat rib cartilage converted into the solid body in FreeCAD (tolerance for
(4 days, 8.5 g) following the general recommendations of sewing was 0.01). Before further conversion, the model
A Tsyb Minority Recruitment and Retention Committee for was manually aligned by the base (Figure 1B). Locations
bioethics of experimental research on laboratory animals. of the future supports (in places of ledges) are shown in
The primary cell culture was obtained according to Gartland Figure 1C and D.
et al. protocol . Briefly, a mixture of 0.25% trypsin, 0.2% 3.2. Support formation procedure
[14]
collagenase II type, and Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s
Medium (DMEM) media (these materials were purchased The supporting part of the scaffold was located only in
from PanEco, Russia) were used to dissolve the cartilage. places of collagen ledges to optimize the printing process
After the first step of isolation, the cleaned ribs were left (printing time and amount of material). Thus, the general
overnight in media with fetal bovine serum (Biosera, outline (overall projection) of the entire thyroid cartilage
France) at 4°C. On the next day, the isolation procedure model on the XY-plane was not changed.
was repeated, and then the cells were washed by two A set of scaffold cross-sections was used to create
cycles of precipitation and resuspension. The chondrocytes the support. For the preliminary estimation, 2 mm step
were cultivated in DMEM (4.5 g/l glucose) with serum, was chosen (Figure 2A). The overall number of slices
penicillin-streptomycin, and glutamine (both were was 17. Each cross-section was extruded to the base of the
purchased from PanEco, Russia) at 4°C and 5% CO . The model. Thus, a general model for collagen and gelatin was
2
cell culture was characterized by Alcian blue stain (Sigma- obtained (Figure 2B). The support model was obtained by
Aldrich) in accordance with Gosset et al. protocol . For a Boolean operation of subtraction the model of thyroid
[15]
the experiment, the second passage was used. cartilage from a general model for collagen and gelatin.
Biocompatibility testing was conducted for The complete supporting part of the scaffold (Figure 2C)
neutralized collagen gel with 40 mg/ml concentration has 23,172 faces and a size of 47.7 × 41.0 × 34.0 mm.
(recommended for the study by the manufacturer) in
contrast to 80 mg/ml hydrogel that was used to verify the 3.2. Influence of cross-section number on the
described technique. The neutralization buffer contains quality of the support
50 mM Tris-HCl and DMEM/F12 medium (pH 8). To The procedure described above included the use of 17
examine collagen biocompatibility, 8 × 8 × 0.2 mm cross-sections with 2 mm step. The number of slices can
scaffolds were printed. Printing parameters and conditions vary depending on the given model. The data on the effect
were the same as for the thyroid cartilage scaffold
fabrication. The cell-laden scaffolds were incubated in A B
the standard conditions for cell cultures. On the 3 and
rd
7 days, the tissue scaffolds were analyzed using a Live/
th
Dead assay (Sigma-Aldrich) according to manufacturer
protocol. The images were processed using ImageJ 1.52.
2.6. Statistics
Cell viability data were analyzed in R 3.5.3 (2019). The D
error of cell viability ratio was assessed in accordance C
with a Poisson distribution. Contingency table and Chi-
square test were used to compare cell viability. The
difference was considered significant at P < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Human thyroid cartilage model
Figure 1. Thyroid cartilage model formation. (A) The area of
The area of interest contouring for each slice was carried interest at DICOM image (marked in red). (B) Model solid body.
out manually (Figure 1A). The creation of the 3D model (C and D) Support material location (yellow). Scale bar – 1 cm.
106 International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 2