Page 98 - IJB-7-3
P. 98
Coaxial Electrohydrodynamic Bioprinting of Pre-Vascularized Tissues
A
B
C
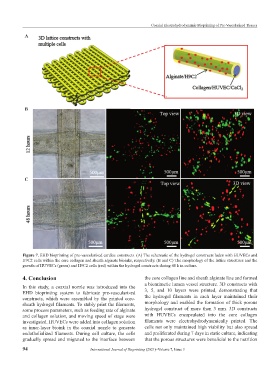
Figure 7. EHD bioprinting of pre-vascularized cardiac constructs. (A) The schematic of the hydrogel constructs laden with HUVECs and
H9C2 cells within the core collagen and sheath alginate bioinks, respectively. (B and C) The morphology of the lattice structures and the
growth of HUVECs (green) and H9C2 cells (red) within the hydrogel constructs during 48 h in culture.
4. Conclusion the core collagen line and sheath alginate line and formed
a biomimetic lumen vessel structure. 3D constructs with
In this study, a coaxial nozzle was introduced into the
EHD bioprinting system to fabricate pre-vascularized 3, 5, and 10 layers were printed, demonstrating that
constructs, which were assembled by the printed core- the hydrogel filaments in each layer maintained their
sheath hydrogel filaments. To stably print the filaments, morphology and enabled the formation of thick porous
some process parameters, such as feeding rate of alginate hydrogel construct of more than 3 mm. 3D constructs
and collagen solution, and moving speed of stage were with HUVECs encapsulated into the core collagen
investigated. HUVECs were added into collagen solution filaments were electrohydrodynamically printed. The
as inner-layer bioink in the coaxial nozzle to generate cells not only maintained high viability but also spread
endothelialized filaments. During cell culture, the cells and proliferated during 7 days in static culture, indicating
gradually spread and migrated to the interface between that the porous structures were beneficial to the nutrition
94 International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 3