Page 186 - IJB-8-3
P. 186
Bioprinting of a Hepatic Tissue Model
A
B
C
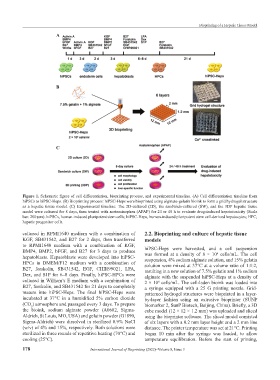
Figure 1. Schematic figure of cell differentiation, bioprinting process, and experimental timeline. (A) Cell differentiation timeline from
hiPSCs to hiPSC-Heps. (B) Bioprinting process: hiPSC-Heps were bioprinted using alginate-gelatin bioink to form a grid hydrogel structure
as a hepatic tissue model. (C) Experimental timeline: The 2D-cultured (2D), the sandwich-cultured (SW), and the 3DP hepatic tissue
model were cultured for 8 days, then treated with acetaminophen (APAP) for 24 or 48 h to evaluate drug-induced hepatotoxicity (Scale
bar: 200 μm). hiPSCs, human-induced pluripotent stem cells; hiPSC-Heps, human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocytes; HPC,
hepatic progenitor cells.
cultured in RPMI1640 medium with a combination of 2.2. Bioprinting and culture of hepatic tissue
KGF, SB431542, and B27 for 2 days, then transferred models
to RPMI1640 medium with a combination of KGF,
BMP4, BMP2, bFGF, and B27 for 3 days to produce hiPSC-Heps were harvested, and a cell suspension
6
hepatoblasts. Hepatoblasts were developed into hiPSC- was formed at a density of 8 × 10 cells/mL. The cell
suspension, 4% sodium alginate solution, and 15% gelatin
HPCs in DMEM/F12 medium with a combination of solution were mixed at 37°C at a volume ratio of 1:1:2,
B27, forskolin, SB431542, EGF, CHIR99021, LPA, resulting in a new solution of 7.5% gelatin and 1% sodium
Dex, and S1P for 6–8 days. Finally, hiPSC-HPCs were alginate with the suspended hiPSC-Heps at a density of
cultured in William’s E medium with a combination of 2 × 10 cells/mL. The cell-laden bioink was loaded into
6
B27, forskolin, and SB431542 for 21 days to completely a syringe equipped with a 25 G printing nozzle. Grid-
mature into hiPSC-Heps. The final hiPSC-Heps were patterned hydrogel structures were bioprinted in a layer-
incubated at 37°C in a humidified 5% carbon dioxide by-layer fashion using an extrusive bioprinter (SUNP
(CO ) atmosphere and passaged every 3 days. To prepare biomarker 2, SunP Biotech, Beijing, China). Briefly, a 3D
2
the bioink, sodium alginate powder (A0682, Sigma- cube model (12 × 12 × 1.2 mm) was uploaded and sliced
Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA) and gelatin powder (G1890, using the bioprinter software. The sliced model consisted
Sigma-Aldrich) were dissolved in sterilized 0.9% NaCl of six layers with a 0.2 mm layer height and a 2 mm line
(w/v) of 4% and 15%, respectively. Both solutions were distance. The printer temperature was set at 21°C. Printing
sterilized in three rounds of repetitive heating (70°C) and began 10 min after the syringe was loaded, to allow
cooling (25°C). temperature equilibration. Before the start of printing,
178 International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 3