Page 111 - IJB-8-4
P. 111
Köpf, et al.
A
B C
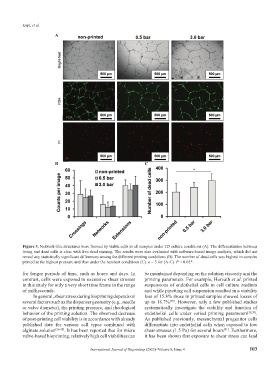
Figure 3. Network-like structures were formed by viable cells in all samples under 2D culture conditions (A). The differentiation between
living and dead cells is clear with live-dead staining. The results were also evaluated with software-based image analysis, which did not
reveal any statistically significant differences among the different printing conditions (B). The number of dead cells was highest in samples
printed at the highest pressure and thus under the harshest conditions (C). n = 3 for (A-C). P < 0.05*.
for longer periods of time, such as hours and days. In be maintained depending on the solution viscosity and the
contrast, cells were exposed to excessive shear stresses printing parameters. For example, Horváth et al. printed
in this study for only a very short time frame in the range suspensions of endothelial cells in cell culture medium
of milliseconds. and while pipetting cell suspension resulted in a viability
In general, shear stress during bioprinting depends on loss of 15.8% those in printed samples showed losses of
several factors such as the dispenser geometry (e.g., needle up to 18.7% . However, only a few published studies
[29]
or valve diameter), the printing pressure, and rheological systematically investigate the viability and function of
behavior of the printing solution. The observed decrease endothelial cells under varied printing parameters [28,30] .
of post-printing cell viability is in accordance with already As published previously, mesenchymal progenitor cells
published data for various cell types combined with differentiate into endothelial cells when exposed to low
alginate solution [26-28] . It has been reported that for micro shear stresses (1.5 Pa) for several hours . Furthermore,
[31]
valve-based bioprinting, relatively high cell viabilities can it has been shown that exposure to shear stress can lead
International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 4 103