Page 112 - IJB-8-4
P. 112
Effect of Bioprinting-Associated Shear Stress and Hydrostatic Pressure
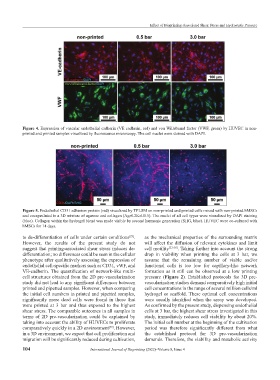
Figure 4. Expression of vascular endothelial cadherin (VE cadherin, red) and von Willebrand factor (VWF, green) by HUVEC in non-
printed and printed samples visualized by fluorescence microscopy. The cell nuclei were stained with DAPI.
Figure 5. Endothelial CD31 adhesion protein (red) visualized by TPLSM on non-printed and printed cells mixed with non-printed hMSCs
and encapsulated in a 3D mixture of agarose and collagen (Agr0.2Koll0.5). The nuclei of all cell types were visualized by DAPI staining
(blue). Collagen within the hydrogel blend was made visible by second harmonic generation (SHG, blue). HUVEC were co-cultured with
hMSCs for 14 days.
to de-differentiation of cells under certain conditions . as the mechanical properties of the surrounding matrix
[23]
However, the results of the present study do not will affect the diffusion of relevant cytokines and limit
suggest that printing-associated shear stress induces de- cell motility [32-36] . Taking further into account the strong
differentiation; no differences could be seen in the cellular drop in viability when printing the cells at 3 bar, we
phenotype after qualitatively assessing the expression of assume that the remaining number of viable and/or
endothelial cell-specific markers such as CD31, vWF, and functional cells is too low for capillary-like network
VE-cadherin. The quantification of network-like multi- formation as it still can be observed at a low printing
cell structures obtained from the 2D pre-vascularization pressure (Figure 2). Established protocols for 3D pre-
study did not lead to any significant differences between vascularization studies demand comparatively high initial
printed and pipetted samples. However, when comparing cell concentrations in the range of several million cells/ml
the initial cell numbers in printed and pipetted samples, hydrogel or scaffold. These optimal cell concentrations
significantly more dead cells were found in those that were usually identified when the assay was developed.
were printed at 3 bar and thus exposed to the highest As confirmed by the present study, dispensing endothelial
shear stress. The comparable outcomes in all samples in cells at 3 bar, the highest shear stress investigated in this
terms of 2D pre-vascularization could be explained by study, immediately reduces cell viability by about 20%.
taking into account the ability of HUVECs to proliferate The initial cell number at the beginning of the cultivation
comparatively quickly in a 2D environment . However, period was therefore significantly different from what
[29]
in a 3D environment, we expect that cell proliferation and the established protocol for 3D pre-vascularization
migration will be significantly reduced during cultivation, demands. Therefore, the viability and metabolic activity
104 International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 4