Page 47 - IJB-8-4
P. 47
Lu, et al.
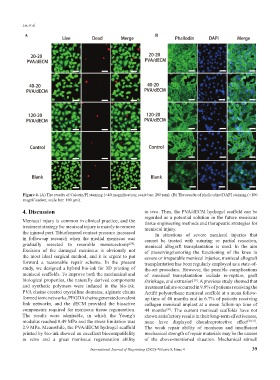
A B
Figure 4. (A) The results of Calcein/PI staining (×40 magnification; scale bar: 200 μm). (B) The results of phalloidine/DAPI staining (×100
magnification; scale bar: 100 μm).
4. Discussion in vivo. Thus, the PVA/dECM hydrogel scaffold can be
regarded as a potential solution in the future meniscus
Meniscal injury is common in clinical practice, and the tissue engineering methods and therapeutic strategies for
treatment strategy for meniscal injury is mainly to remove meniscal injury.
the injured part. Tibiofemoral contact pressure increased In situations of severe meniscal injuries that
in follow-up research when the medial meniscus was cannot be treated with suturing or partial resection,
gradually resected to resemble meniscectomy . meniscal allograft transplantation is used. In the aim
[28]
Excision of the damaged meniscus is obviously not of preserving/restoring the functioning of the knee in
the most ideal surgical method, and it is urgent to put severe or irreparable meniscal injuries, meniscal allograft
forward a reasonable repair scheme. In the present transplantation has been regularly employed as a state-of-
study, we designed a hybrid bio-ink for 3D printing of the-art procedure. However, the possible complications
meniscal scaffolds. To improve both the mechanical and of meniscal transplantation include re-rupture, graft
biological properties, the naturally derived components shrinkage, and extrusion . A previous study showed that
[29]
and synthetic polymers were induced in the bio-ink. treatment failure occurred in 9.9% of patients receiving the
PVA chains created crystalline domains, alginate chains Actifit polyurethane meniscal scaffold at a mean follow-
formed ionic networks, PEGDA chains generated covalent up time of 40 months and in 6.7% of patients receiving
link networks, and the dECM provided the bioactive collagen meniscal implant at a mean follow-up time of
components required for meniscus tissue regeneration. 44 months . The current meniscal scaffolds have not
[30]
The results were admirable, in which the Young’s shown satisfactory results in their long-term effectiveness,
modulus reached 0.49 MPa and the stress limitation was none have displayed chondroprotective effect [20,31] .
2.9 MPa. Meanwhile, the PVA/dECM hydrogel scaffold The weak repair ability of meniscus and insufficient
printed by bio-ink showed an excellent biocompatibility mechanical strength of repair materials may be the causes
in vitro and a great meniscus regeneration ability of the above-mentioned situation. Mechanical stimuli
International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 4 39