Page 14 - IJB-9-1
P. 14
International Journal of Bioprinting Biocompatible materials and Multi Jet Fusion
Figure 5. The results of amplitude sweeps of bioinks F, D, and G (increasing CCNC content: 1.0%, 1.4%, 2.0%).
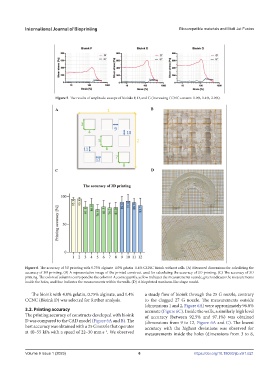
Figure 6. The accuracy of 3D printing with 0.75% alginate_4.0% gelatin_1.4% CCNC bioink without cells. (A) Measured dimensions for calculating the
accuracy of 3D printing. (B) A representative image of the printed construct used for calculating the accuracy of 3D printing. (C) The accuracy of 3D
printing. The colors of columns correspond to the colors in A; consequently, yellow indicates the measurements outside, green indicates the measurements
inside the holes, and blue indicates the measurements within the walls. (D) A bioprinted meniscus-like shape model.
The bioink with 4.0% gelatin, 0.75% alginate, and 1.4% a steady flow of bioink through the 25 G nozzle, contrary
CCNC (Bioink D) was selected for further analysis. to the clogged 27 G nozzle. The measurements outside
(dimensions 1 and 2, Figure 6A) were approximately 96.0%
3.2. Printing accuracy accurate (Figure 6C). Inside the walls, a similarly high level
The printing accuracy of constructs developed with bioink of accuracy (between 92.5% and 97.1%) was obtained
D was compared to the CAD model (Figure 6A and B). The (dimensions from 9 to 12, Figure 6A and C). The lowest
best accuracy was obtained with a 25 G nozzle that operates accuracy with the highest deviations was observed for
at 40–55 kPa with a speed of 22–30 mm·s . We observed measurements inside the holes (dimensions from 3 to 8,
−1
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2023) 6 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i1.621