Page 374 - IJB-9-1
P. 374
International Journal of Bioprinting Micro/nano-3D hemostats for rapid wound healing
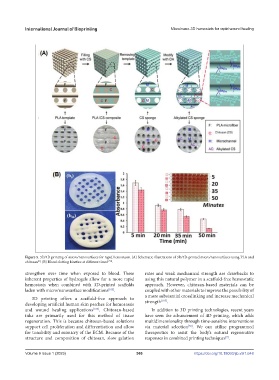
Figure 5. 3D/4D printing of micro/nanosurfaces for rapid hemostasis. (A) Schematic illustrations of 3D/4D-printed micro/nanosurfaces using PLA and
chitosan . (B) Blood clotting kinetics at different times [153] .
[3]
strengthen over time when exposed to blood. These rates and weak mechanical strength are drawbacks to
inherent properties of hydrogels allow for a more rapid using this natural polymer in a scaffold-free hemostatic
hemostasis when combined with 3D-printed scaffolds approach. However, chitosan-based materials can be
laden with micro/nanosurface modifications [103] . coupled with other materials to improve the possibility of
a more substantial crosslinking and increase mechanical
3D printing offers a scaffold-free approach to [105]
developing artificial human skin patches for hemostasis strength .
and wound healing applications [104] . Chitosan-based In addition to 3D printing technologies, recent years
inks are primarily used for this method of tissue have seen the advancement of 4D printing, which adds
regeneration. This is because chitosan-based solutions multidimensionality through time-sensitive interventions
support cell proliferation and differentiation and allow via material selection . We can utilize programmed
[50]
for tunability and mimicry of the ECM. Because of the therapeutics to assist the body’s natural regenerative
structure and composition of chitosan, slow gelation responses in combined printing techniques .
[7]
V
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2023)olume 9 Issue 1 (2023) 366 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i1.648