Page 369 - IJB-9-1
P. 369
International Journal of Bioprinting Micro/nano-3D hemostats for rapid wound healing
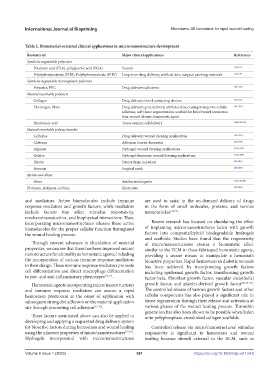
Table 2. Biomaterial-oriented clinical applications in micro/nanostructure development
Biomaterial Major clinical applications References
Synthetic degradable polyesters
Polylactic acid (PLA), polyglycolic acid (PGA) Sutures [176,177]
Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB), Polyhydroxyvalerate (PHV) Long-term drug delivery; artificial skin; surgical patching materials [178,179]
Synthetic degradable thermoplastic polymers
Polyester, PVC Drug delivery; adhesives [180-182]
Natural resorbable polymers
Collagen Drug delivery; blood contacting devices [183,184]
Fibrinogen, fibrin Drug delivery; gene delivery; artificial skin; coating to improve cellular [185-187]
adhesion; soft tissue augmentation; scaffold for blood vessel reconstruc-
tion; wound closure; hemostatic agent
Hyaluronic acid Tissue sealant; cell delivery [186,188-190]
Natural resorbable polysaccharides
Cellulose Drug delivery; wound dressing applications [191-193]
Chitosan Adhesion barrier; hemostat [194-198]
Alginate Hydrogel; wound dressing applications [53,55,199]
Gelatin Hydrogel; hemostat; wound dressing applications [7,124,200]
Elastin Hemorrhage impedant [201-203]
Heparin Surgical mesh [204-206]
Metals and alloys
Silver Antibacterial agents [131,140,168]
Platinum, platinum–iridium Electrodes [207-209]
and mediators. Active biomolecules include immune are used to assist in the on-demand delivery of drugs
response mediators and growth factors, while mediators in the form of small molecules, proteins, and various
include factors that affect stimulus responsivity, nanoparticles [74,75] .
mechanotransduction, and biophysical interactions. Thus,
incorporating micro/nanostructures releases these active Recent research has focused on elucidating the effect
biomolecules for the proper cellular function throughout of implanting micro/nanostructures laden with growth
the wound healing process. factors into composite/hybrid biodegradable hydrogels
and scaffolds. Studies have found that the responsivity
Through current advances in elucidation of material of micro/nanostructures creates a biomimetic effect
properties, we can see that there has been improved micro/ similar to the ECM in these fabricated hemostatic agents,
nanostructure functionality as hemostatic agents, including providing a secure means to manipulate a hemostat’s
the incorporation of various immune response mediators bioactive properties. Rapid hemostasis in diabetic wounds
in their design. These immune response mediators promote has been achieved by incorporating growth factors
cell differentiation and direct macrophage differentiation including epidermal growth factor, transforming growth
to pro- and anti-inflammatory phenotypes [70,71] . factor-beta, fibroblast growth factor, vascular endothelial
Hemostatic agents incorporating micro/nanostructures growth factor, and platelet-derived growth factor [45,76-78] .
and immune response mediators can ensure a rapid The controlled release of various growth factors and other
hemostasis promotion at the onset of application with cellular components has also played a significant role in
subsequent strong clot adhesion on the material application tissue regeneration through their release and activation at
site through promoting cell adhesion [63-65] . various phases of the wound healing process. Thrombin
generation has also been shown to be possible when laden
These factors mentioned above can also be applied to onto polyphosphate-crosslinked collagen scaffolds.
developing and applying a sequential drug delivery system
for bioactive factors during hemostasis and wound healing Controlled release via micro/nanostructures’ stimulus
using the inherent properties of micro/nanostructures [72,73] . responsivity is significant to hemostasis and wound
Hydrogels incorporated with micro/nanostructures healing because stimuli external to the ECM, such as
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2023)olume 9 Issue 1 (2023)
V 361 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i1.648