Page 371 - IJB-9-1
P. 371
International Journal of Bioprinting Micro/nano-3D hemostats for rapid wound healing
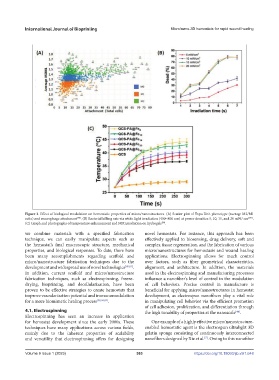
Figure 3. Effect of biological modulation on hemostatic properties of micro/nanostructures. (A) Scatter plot of Topo Unit phenotype (average M2/M1
ratio) and macrophage attachment . (B) Bacterial killing rate via white light irradiation (400–800 nm) at power densities 5, 10, 15, and 20 mW/ cm 2[71] .
[70]
(C) Graph and photographs of temperature enhancement and NIR irradiation on hydrogels .
[79]
we combine materials with a specified fabrication novel hemostats. For instance, this approach has been
technique, we can easily manipulate aspects such as effectively applied to biosensing, drug delivery, soft and
the hemostat’s final macroscopic structure, mechanical complex tissue regeneration, and the fabrication of various
properties, and biological responses. To date, there have micro/nanostructures for hemostasis and wound healing
been many accomplishments regarding scaffold and applications. Electrospinning allows for much control
micro/nanostructure fabrication techniques due to the over factors, such as fiber geometrical characteristics,
development and widespread use of novel technologies [80,81] . alignment, and architecture. In addition, the materials
In addition, current scaffold and micro/nanostructure used in the electrospinning and manufacturing processes
fabrication techniques, such as electrospinning, freeze- influence a nanofiber’s level of control in the modulation
drying, bioprinting, and decellularization, have been of cell behaviors. Precise control in manufacture is
proven to be effective strategies to create hemostats that beneficial for applying micro/nanostructures in hemostat
improve vascularization potential and immunomodulation development, as electrospun nanofibers play a vital role
for a more biomimetic healing process [38,58,82] . in manipulating cell behavior via the efficient promotion
of cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation through
4.1. Electrospinning the high tunability of properties at the nanoscale .
[44]
Electrospinning has seen an increase in application
for hemostat development since the early 2000s. These One example of a highly effective micro/nanostructure-
techniques have many applications across various fields, enabled hemostatic agent is the electrospun ultralight 3D
mainly due to the inherent properties of scalability gelatin sponge consisting of continuously interconnected
and versatility that electrospinning offers for designing nanofibers designed by Xie et al. . Owing to this nanofiber
[7]
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2023)olume 9 Issue 1 (2023)
V 363 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i1.648