Page 384 - IJB-9-2
P. 384
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D gel-printed β-TCP/TiO2 porous scaffolds for cancellous bone tissue engineering
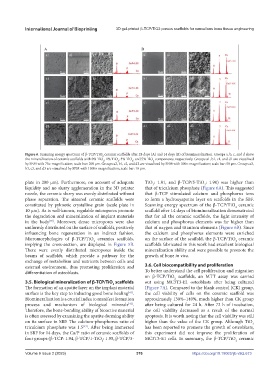
Figure 6. Scanning energy spectrum of β-TCP/TiO ceramic scaffolds after 28 days (A) and 14 days (B) of biomineralization. Groups a, b, c, and d show
2
the mineralization of ceramic scaffolds with 0% TiO , 1% TiO , 3% TiO , and 5% TiO components, respectively. Groups a1, b1, c1, and d1 are visualized
2
2
2
2
by SEM with 75× magnification; scale bar: 200 μm. Groups a2, b1, c2, and d2 are visualized by SEM with 300× magnification; scale bar: 50 μm. Groups a3,
b3, c3, and d3 are visualized by SEM with 1500× magnification; scale bar: 10 μm.
plate in 200 μm). Furthermore, on account of adequate TiO : 1.81, and β-TCP/5-TiO : 1.90) was higher than
2
2
liquidity and no slurry agglomeration in the 3D printer that of tricalcium phosphate (Figure 6A). This suggested
nozzle, the ceramic slurry was evenly distributed without that β-TCP stimulated calcium and phosphorus ions
phase separation. The sintered ceramic scaffolds were to form a hydroxyapatite layer on scaffolds in the SBF.
constituted by pyknotic crystalline grain (scale plate in Scanning energy spectrum of the β-TCP/TiO ceramic
2
10 µm). As is well-known, regulable micropores promote scaffold after 14 days of biomineralization demonstrated
the degradation and mineralization of implant materials that for all the ceramic scaffolds, the light intensity of
in the body . Moreover, dense micropores were also calcium and phosphorus elements was far higher than
[39]
uniformly distributed on the surface of scaffolds, positively that of oxygen and titanium elements (Figure 6B). Since
influencing bone regeneration in an indirect fashion. the calcium and phosphorus elements were enriched
Micromorphologies of β-TCP/TiO ceramics scaffolds, on the surface of the scaffold, the β-TCP/TiO ceramic
2
2
implying the cross-section, are displayed in Figure 5B. scaffolds fabricated in this work had excellent biological
There were evenly distributed micropores inside the mineralization ability and were possible to promote the
beams of scaffolds, which provide a pathway for the growth of bone in vivo.
exchange of metabolism and nutrients between cells and
external environment, thus promoting proliferation and 3.6. Cell biocompatibility and proliferation
differentiation of osteoblasts. To better understand the cell proliferation and migration
on β-TCP/TiO scaffolds, an MTT assay was carried
2
3.5. Biological mineralization of β-TCP/TiO scaffolds out using MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts after being cultured
2
The formation of an apatite layer on the implant material (Figure 7A). Compared to the blank control (CK) group,
surface is the key step to inducing good bone healing [41] . the cell viability of cells on the ceramic scaffold was
Biomineralization is a crucial index to manifest formation approximately 130%–140%, much higher than CK group
process and mechanism of biological minerals [42] . after being cultured for 24 h. After 72 h of incubation,
Therefore, the bone-bonding ability of bioactive material the cell viability decreased as a result of the normal
is often assessed by examining the apatite-forming ability apoptosis. It is worth noting that the cell viability was still
on its surface in SBF. The calcium-phosphorus ratio of higher than the value of the CK group. Although TiO 2
tricalcium phosphate was 1.5 [43] . After being immersed has been reported to promote the growth of osteoblasts,
in SBF for 14 days, the Ca/P ratio of ceramic scaffolds of this experiment did not improve the proliferation of
four groups (β-TCP: 1.94, β-TCP/1-TiO : 1.95, β-TCP/3- MC3T3-E1 cells. In summary, the β-TCP/TiO ceramic
2
2
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 376 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.673