Page 89 - IJB-9-2
P. 89
International Journal of Bioprinting Steam-sterilized and degradable FFF-printed PLA/PHA surgical guides
A B
D
C
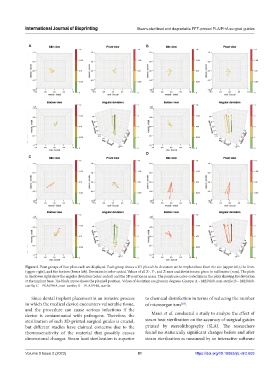
Figure 5. Four groups of four plots each are displayed. Each group shows a 3D plot of the deviation at the implant base from the site (upper left), the front
(upper right), and the bottom (lower left). Deviation is color-coded. Values of all X-, Y-, and Z-axes and deviation are given in millimeter (mm). The plots
in the lower right show the angular deviation (color-coded) and the 3D position in space. The points are color-coded like in the plots showing the deviation
at the implant base. The black arrow shows the planned position. Values of deviation are given in degrees. Groups: A – MED610, non-sterile; B – MED610,
sterile; C – PLA/PHA, non-sterile; D – PLA/PHA, sterile.
Since dental implant placement is an invasive process to chemical disinfection in terms of reducing the number
in which the medical device encounters vulnerable tissue, of microorganisms .
[23]
and the procedure can cause serious infections if the
device is contaminated with pathogens. Therefore, the Marei et al. conducted a study to analyze the effect of
sterilization of such 3D-printed surgical guides is crucial, steam heat sterilization on the accuracy of surgical guides
but different studies have claimed concerns due to the printed by stereolithography (SLA). The researchers
thermosensitivity of the material that possibly causes found no statistically significant changes before and after
dimensional changes. Steam heat sterilization is superior steam sterilization as measured by an interactive software
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 81 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.655