Page 87 - IJB-9-2
P. 87
International Journal of Bioprinting Steam-sterilized and degradable FFF-printed PLA/PHA surgical guides
A B placement, CBCT-image of the model with the implant
was acquired and the DICOM-dataset was transferred to
coDiagnostiX for analysis of the implant position.
2.5. Deviation measurement
C D The treatment evaluation tool from coDiagnostiX software
was used to compare the planned and the achieved implant
position. The post-treatment CBCT image was used to
create a virtual model. This model was automatically and
manually matched with the original planning model. In
the next step, the position of the achieved implant was
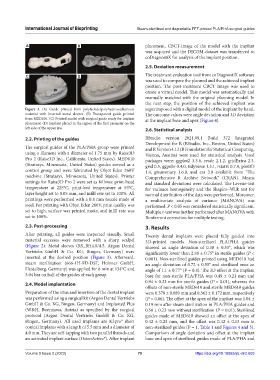
Figure 3. (A) Guide printed from polylactide/polyhydroxyalkanoate superimposed with a digital model of the implant by hand.
material with inserted metal sleeves. (B) Transparent guide printed The outcome values were angle deviation and 3D deviation
from MED610. (C) Printed model with surgical guide ready for implant at the implant base and apex (Figure 4).
placement. (D) Implant placed in the region of the first premolar on the
left side of the upper jaw. 2.6. Statistical analysis
2.2. Printing of the guides RStudio version 2021.09.1 Build 372 Integrated
Development for R (RStudio, Inc., Boston, United States)
The surgical guides of the PLA/PHA group were printed and R Version 4.12 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing,
using a filament with a diameter of 1.75 mm by Raise3D Vienna, Austria) were used for statistical analysis. Used
Pro 2 (Raise3D Inc., California, United States). MED610 packages were: ggplot2 3.3.6, readr 2.1.2, gridExtra 2.3,
(Stratasys, Minnesota, United States) guides served as a grid 0.5, ggpubr 0.4.0, tidyverse 1.3.1, rstatix 0.7.0, plot3D
control group and were fabricated by Objet Eden 260V 1.4, gtsummary 1.6.0, and car 3.0 available from “The
machine (Stratasys, Minnesota, United States). Printer Comprehensive R Archive Network” (CRAN). Means
settings for Raise3D Pro 2 were set as follows: print-head and standard deviations were calculated. The Levene-test
temperature at 225°C, print-bed temperature at 55°C, for variance homogeneity and the Shapiro–Wilk test for
layer height set to 0.05 mm, and infill rate set to 100%. All normal distribution of the data were performed. Moreover,
printings were performed with a 0.4 mm nozzle made of a multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) was
steel. For printing with Objet Eden 260V, print quality was performed. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
set to high, surface was printed matte, and infill rate was Multiple t-test was further performed after MANOVA with
set to 100%. Bonferroni correction for multiple testing.
2.3. Post-processing 3. Results
After printing, all guides were inspected visually. Small Twenty dental implants were placed fully guided into
material excesses were removed with a sharp scalpel 3D-printed models. Non-sterilized PLA/PHA guides
(Figure 2). Metal sleeves (RS_BH4.0/4.5, Argon Dental showed an angle deviation of 0.38 ± 0.53°, which was
Vertriebs GmbH & Co. KG, Bingen, Germany) were significantly lower than 2.88 ± 0.75° in sterile guides (P <
inserted at the desired position (Figure 3). Afterward, 0.001). Non-sterilized guides printed using MED610 had
steam sterilization (666-1H-FD-DST, Holzner GmbH, an angle deviation of 0.72 ± 0.55° and sterilized ones an
Heidelberg, Germany) was applied for 8 min at 134°C and angle of 1.1 ± 0.77° (P = 0.4). The 3D offset at the implant
3.04 bar on half of the guides of each group. base for non-sterile PLA/PHA was 0.49 ± 0.21 mm and
2.4. Model implantation 0.94 ± 0.23 mm for sterile guides (P = 0.01), whereas the
offsets of non-sterile MED610 and sterile MED610 guides
Preparation of the situs and insertion of the dental implant were 0.378 ± 0.089 mm and 0.362 ± 0.172 mm, respectively
was performed using a surgical kit (Argon Dental Vertriebs (P = 0.86). The offset at the apex of the implant was 1.04 ±
GmbH & Co. KG, Bingen, Germany) and Implanted Plus 0.19 mm after steam sterilization in PLA/PHA guides and
(W&H, Buermoos, Autria) as specified by the surgical 0.50 ± 0.23 mm without sterilization (P = 0.01). Sterilized
protocol (Argon Dental Vertriebs GmbH & Co. KG, guides made of MED610 showed an offset at the apex of
Bingen, Germany). All used implants are K3pro® short 0.42 ± 0.23 mm, and the offset was 0.42 ± 0.13 mm in
conical implants with a length of 5.5 mm and a diameter of non-sterilized guides (P = 1, Table 1 and Figures 4 and 5).
4.0 mm. They are self-tapping with two parallel threads and Comparison of angle deviation and offset at the implant
an activated implant surface (OsteoActive®). After implant base and apex of sterilized guides made of PLA/PHA and
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 79 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.655