Page 90 - IJB-9-2
P. 90
International Journal of Bioprinting Steam-sterilized and degradable FFF-printed PLA/PHA surgical guides
A B
C
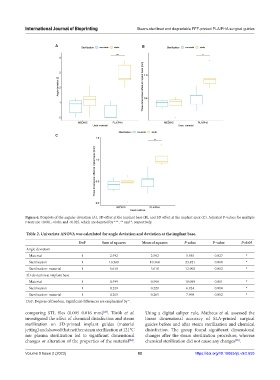
Figure 6. Boxplots of the angular deviation (A), 3D offset at the implant base (B), and 3D offset at the implant apex (C). Adjusted P-values for multiple
t-tests are <0.001, <0.01, and <0.025, which are denoted by ***, ** and *, respectively.
Table 2. Univariate ANOVA was calculated for angle deviation and deviation at the implant base.
DoF Sum of squares Mean of squares F‑value P‑value P<0.05
Angle deviation
Material 1 2.592 2.592 5.955 0.027 *
Sterilization 1 10.368 10.368 23.821 0.000 *
Sterilization: material 1 5.618 5.618 12.908 0.002 *
3D deviation at implant base
Material 1 0.599 0.599 18.099 0.001 *
Sterilization 1 0.229 0.229 6.924 0.018 *
Sterilization: material 1 0.265 0.265 7.998 0.012 *
DoF: Degrees of freedom. Significant differences are emphasized by *.
comparing STL files (0.005–0.016 mm) . Török et al. Using a digital caliper rule, Matheus et al. assessed the
[23]
investigated the effect of chemical disinfection and steam linear dimensional accuracy of SLA-printed surgical
sterilization on 3D-printed implant guides (material guides before and after steam sterilization and chemical
jetting) and showed that neither steam sterilization at 121°C disinfection. The group found significant dimensional
nor plasma sterilization led to significant dimensional changes after the steam sterilization procedure, whereas
changes or alteration of the properties of the material . chemical sterilization did not cause any changes .
[24]
[25]
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 82 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.655