Page 213 - IJB-9-3
P. 213
International Journal of Bioprinting Dual ions mixed GelMA for hair follicle regeneration
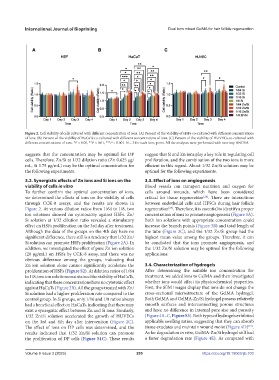
Figure 2. Cell viability of cells cultured with different concentration of ions. (A) Percent of the viability of HSFs co-cultured with different concentrations
of ions. (B) Percent of the viability of HaCaTs co-cultured with different concentrations of ions. (C) Percent of the viability of HUVECs co-cultured with
different concentrations of ions. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. N = 3 for each time point. All the analyses were performed with two-way ANOVA.
suggests that the concentration may be optimal for DP suggest that Si and Zn ions play a key role in regulating cell
cells. Therefore, Zn/Si at 1/32 dilution ratio (Zn 0.625 μg/ proliferation, and the combination of the two ions is more
mL, Si 3.75 μg/mL) may be the optimal concentration for efficient in this regard. About 1/32 Zn/Si solution may be
the following experiments. optimal for the following experiments.
3.2. Synergistic effects of Zn ions and Si ions on the 3.3. Effect of ions on angiogenesis
viability of cells in vitro Blood vessels can transport nutrition and oxygen for
To further confirm the optimal concentration of ions, cells around wounds, which have been considered
we determined the effects of ions on the viability of cells critical for tissue regeneration . There are interactions
[28]
through CCK-8 assays, and the results are shown in between endothelial cells and HFSCs during hair follicle
Figure 2. At various dilution ratios from 1/64 to 1/8, two regeneration . Therefore, it is essential to identify a proper
[27]
ion solutions showed no cytotoxicity against HSFs. Zn/ concentration of ions to promote angiogenesis (Figure 3A).
Si solution at 1/32 dilution ratio revealed a stimulatory Both ion solutions with appropriate concentration could
effect on HSFs proliferation on the 3rd day after treatment. increase the branch points (Figure 3B) and total length of
Although the data of the groups on the 4th day have no the tube (Figure 3C), and the 1/32 Zn/Si group had the
significant difference, there still is a tendency that 1/32 Zn/ highest mean value among the groups. Therefore, it can
Si solution can promote HSFs proliferation (Figure 2A). In be concluded that the ions promote angiogenesis, and
addition, we investigated the effect of pure Zn ion solution the 1/32 Zn/Si solution may be optimal for the following
(20 μg/mL) on HSFs by CCK-8 assay, and there was no applications.
obvious difference among the groups, indicating that
Zn ion solution alone cannot significantly accelerate the 3.4. Characterization of hydrogels
proliferation of HSFs (Figure S2). At dilution ratios of 1/64 After determining the suitable ion concentration for
to 1/8, two ion solutions maintained the viability of HaCaTs, treatment, we added ions to GelMA and then investigated
indicating that these concentrations have no cytotoxic effect whether ions would affect its physicochemical properties.
against HaCaTs (Figure 2B). All the groups treated with Zn/ First, the SEM images display that ions do not change the
Si solution had a higher proliferation rate compared to the cross-sectional microstructure of the GelMA hydrogel.
control group. In Si groups, only 1/16 and 1/8 ratios always Both GelMA and GelMA-Zn/Si hydrogel possess relatively
had a beneficial effect on HaCaTs, indicating that there may smooth surfaces and interconnecting porous structures
exist a synergistic effect between Zn and Si ions. Similarly, and have no difference in internal pore size and porosity
1/32 Zn/Si solution accelerated the growth of HUVECs (Figure 4A–C, Figure S3). Both types of hydrogels exhibited
on the 3rd and 4th day after intervention (Figure 2C). applicable swelling ratios, suggesting that they can absorb
[19]
The effect of ions on DP cells was determined, and the tissue exudates and maintain wound moist (Figure 4D) .
results indicated that 1/32 Zn/Si solution can promote As for degradation in vitro, GelMA-Zn/Si hydrogel still had
the proliferation of DP cells (Figure S1C). These results a faster degradation rate (Figure 4E). As compared with
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2023) 205 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.703