Page 226 - IJB-9-3
P. 226
International Journal of Bioprinting Biomaterials for vascularized and innervated tissue regeneration
[21]
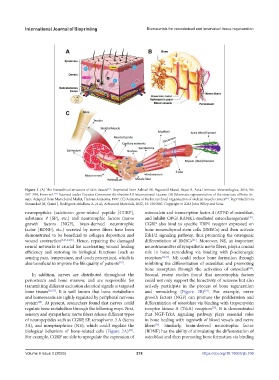
Figure 1. (A) The hierarchical structure of skin tissues . Reprinted from Ashrafi M, Baguneid Mand, Bayat A, Acta Dermato-Venereologica, 2016, 96:
[21]
587–594, From ref. licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. (B) Schematic representation of the structure of bone tis-
[41]
sues. Adapted from Marieb and Mallet, Human Anatomy, 1997. (C) Anatomy of the hierarchical organization of skeletal muscle tissues . Reprinted from
Samandari M, Quint J, Rodriguez-delaRosa A, et al., Advanced Materials, 2022, 34: 2105883. Copyright © 2022 John Wiley and Sons.
neuropeptides (calcitonin gene-related peptide [CGRP], osteocalcin and transcription factor-4 (ATF4) of osteoblast,
substance P [SP], etc.) and neurotrophic factors (nerve and inhibit OPG/ RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis .
[30]
growth factors [NGF], brain-derived neurotrophic CGRP also bind to specific TRP1 receptor expressed on
factor [BDNF], etc.) secreted by nerve fibers have been bone mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) and then activate
demonstrated to be beneficial to collagen deposition and Erk1/2 signaling pathway, thus promoting the osteogenic
wound contraction [3,21,23,25] . Hence, repairing the damaged differentiation of BMSCs . Moreover, NE, an important
[31]
neural networks is crucial for accelerating wound healing neurotransmitter of sympathetic nerve fibers, plays a crucial
efficiency and restoring its biological functions (such as role in bone remodeling via binding with β-adrenergic
sensing pain, temperature, and touch perception), which is receptors [32,33] . NE could reduce bone formation through
also beneficial to improve the life quality of patients . inhibiting the differentiation of osteoblast and promoting
[19]
bone resorption through the activation of osteoclast .
[34]
In addition, nerves are distributed throughout the Second, recent studies found that neurotrophic factors
periosteum and bone marrow, and are responsible for could not only support the bioactivity of neurons but also
transmitting different excitation electrical signals to targeted actively participate in the process of bone regeneration
bone tissues [26,27] . It is well known that bone metabolism and remodeling (Figure 2B) . For example, nerve
[10]
and homeostasis are tightly regulated by peripheral nervous growth factors (NGF) can promote the proliferation and
system . At present, researchers found that nerves could differentiation of osteoblast via binding with tropomyosin
[28]
regulate bone metabolism through the following ways. First, receptor kinase A (TrkA) receptors . It is demonstrated
[35]
sensory and sympathetic nerve fibers release different types that NGF-TrkA signaling pathway plays essential roles
of neuropeptides such as CGRP, SP, semaphorin 3 A (Sema in bone healing with ingrowth of blood vessels and nerve
3A), and norepinephrine (NE), which could regulate the fibers . Similarly, brain-derived neurotrophic factor
[36]
biological behaviors of bone-related cells (Figure 2A) . (BDNF) has the ability of stimulating the differentiation of
[29]
For example, CGRP are able to upregulate the expression of osteoblast and then promoting bone formation via binding
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2023) 218 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.706