Page 326 - IJB-9-3
P. 326
International Journal of Bioprinting New fibrillar collagen for 3D printing and bioprinting
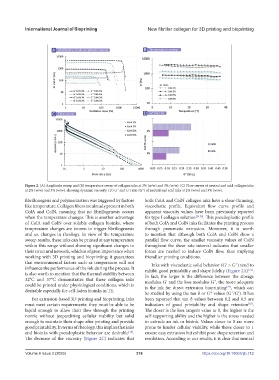
Figure 2. (A) Amplitude sweep and (B) temperature sweep of collagen inks at 2% (w/w) and 3% (w/w). (C) Flow curves of neutral and acid collagen inks
at 2% (w/w) and 3% (w/w), showing dynamic viscosity. (D) G˝ and Gʹ ratio (G*) of neutral and acid inks at 2% (w/w) and 3% (w/w).
fibrillonegesis and polymerization was triggered by factors both ColA and ColN collagen inks have a shear-thinning,
like temperature. Collagen fibers are already present in both viscoelastic profile. Equivalent flow curve profile and
ColA and ColN, meaning that no fibrillogenesis occurs apparent viscosity values have been previously reported
when the temperature changes. This is another advantage for type I collagen solution [29,30] . This pseudoplastic profile
of ColA and ColN over soluble collagen bioinks, where of both ColA and ColN inks facilitates the printing process
temperature changes are known to trigger fibrillogenesis through pneumatic extrusion. Moreover, it is worth
and so, changes in rheology. In view of the temperature to mention that although both ColA and ColN show a
sweep results, these inks can be printed at any temperature parallel flow curve, the smaller viscosity values of ColN
within this range without showing significant changes in throughout the shear rate interval indicates that smaller
their structural network, which is of great importance when forces are needed to induce ColN flow, thus implying
working with 3D printing and bioprinting; it guarantees friendlier printing conditions.
that environmental factors such as temperature will not Inks with viscoelastic solid behavior (Gʹ > G˝) tend to
influence the performance of the ink during the process. It exhibit good printability and shape fidelity (Figure 2A) .
[31]
is also worth to mention that the thermal stability between In fact, the larger is the difference between the storage
32°C and 37°C demonstrates that these collagen inks modulus Gʹ and the loss modulus G˝, the more adequate
could be printed under physiological conditions, which is is the ink for direct extrusion bioprinting , which can
[24]
desirable especially for cell-laden bioinks in TE.
be studied by using the tan δ or G* values (G˝/Gʹ). It has
For extrusion-based 3D printing and bioprinting, inks been reported that tan δ values between 0.2 and 0.5 are
must meet certain requirements: they must be able to be indicators of good printability and shape retention .
[32]
liquid enough to allow their flow through the printing The closer is the loss tangent value to 0, the higher is the
nozzle without jeopardizing cellular viability but solid self-supporting ability and the higher is the stress needed
enough to maintain their shape after printing and provide to extrude an ink or bioink. Values closer to 0 are more
good printability. In terms of rheology, this implies that inks prone to hinder cellular viability, while those closer to 1
and bioinks with pseudoplastic behavior are desirable . ensure easy extrusion but exhibit poor shape retention and
[13]
The decrease of the viscosity (Figure 2C) indicates that resolution. According to our results, it is clear that neutral
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2023) 318 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.712