Page 93 - IJB-9-3
P. 93
International Journal of Bioprinting Biocompatible 3D printing photosensitive resin
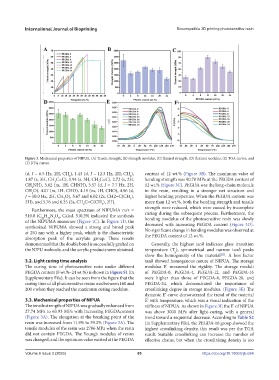
Figure 3. Mechanical properties of NIPUA. (A) Tensile strength, (B) strength modulus, (C) flexural strength, (D) flexural modulus, (E) TGA curves, and
(F) DTG curves.
(d, J = 6.5 Hz, 2H, CH ), 1.43 (d, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H, CH ), content of 12 wt.% (Figure 3B). The maximum value of
2
2
1.87 (s, 3H, CH C=C), 1.94 (s, 3H, CH C=C), 2.72 (s, 2H, bending strength was 90.78 MPa at the PEGDA content of
3
3
CH NH), 3.02 (m, 1H, CHNH), 3.57 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H, 12 wt.% (Figure 3C). PEGDA was the long-chain molecule
2
CH O), 4.07 (m, 1H, CHO), 4.19 (m, 1H, CHO), 4.96 (d, in the resin, resulting in a stronger net structure and
2
J = 10.0 Hz, 2H, CH O), 5.67 and 6.02 (2s, CH2=C(CH ), higher bending properties. When the PEGDA content was
2
3
2H), and 5.76 and 6.25 (2s, CH C=C(CH ), 2H). more than 12 wt.%, both the bending strength and tensile
2 3
Furthermore, the mass spectrum of NIPUMA m/z = strength were reduced, which were caused by incomplete
510.8 (C H N O , Calcd. 510.29) indicated the synthesis curing during the subsequent process. Furthermore, the
bending modulus of the photosensitive resin was slowly
26
42
2
8
of the NIPUMA monomer (Figure 1C). In Figure 1D, the decreased with increasing PEGDA content (Figure 3D).
synthesized NIPUMA showed a strong and broad peak No significant change in bending modulus was observed at
at 250 nm with a higher peak, which is the characteristic the PEGDA content of 12 wt.%.
absorption peak of the acrylate group. These results
demonstrated that the double bond is successfully grafted on Generally, the highest tanδ indicates glass transition
the NIPU molecule, and the acrylic products were obtained. temperature (T ), symmetrical and narrow tanδ peaks
g
show the homogeneity of the material . A loss factor
[22]
3.2. Light curing time analysis tanδ showed homogenous nature of NIPUA. The storage
The curing time of photosensitive resin under different modulus E’ measured the rigidity. The storage moduli
PEGDA content (0 wt.%–24 wt.%) is shown in Figure S1 (in of PEGDA-0, PEGDA-4, PEGDA-12, and PEGDA-16
Supplementary File). It can be seen from the figure that the were higher than those of PEGDA-8, PEGDA-20, and
curing time of all photosensitive resins was between 160 and PEGDA-24, which demonstrated the importance of
200 s when they reached the maximum curing modulus. crosslinking degree in storage modulus. (Figure 3E) The
dynamic E’ curve demonstrated the trend of the material
3.3. Mechanical properties of NIPUA E’ with temperature, which was a visual indication of the
The tensile strength of NIPUA was gradually enhanced from stiffness of NIPUA. As shown in Figure 3F, the E’ of NIPUA
27.74 MPa to 63.93 MPa with increasing PEGDAcontent was above 3000 MPa after light-curing, with a general
(Figure 3A). The elongation at the breaking point of the trend toward a sequential decrease. According to Table S2
resin was increased from 11.9% to 59.2% (Figure 3A). The (in Supplementary File), the PEGDA-16 group showed the
tensile modulus of the resin was 2706 MPa when the resin highest crosslinking density, this result was per the TGA
did not contain PEGDA. The Young’s modulus of resins result. Suitable crosslinking can increase the number of
was changed, and the optimum value existed at the PEGDA effective chains, but when the crosslinking density is too
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2023) 85 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.684