Page 419 - IJB-9-4
P. 419
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D bioprinting of artificial blood vessel
A B
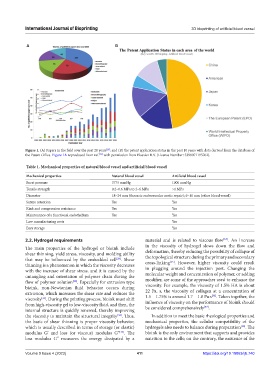
Figure 1. (A) Papers in the field over the past 20 years ; and (B) the patent application status in the past 10 years with data derived from the database of
[23]
the Patent Office. Figure 1A reproduced from ref. with permission from Elsevier B.V. (License Number: 5398071195762).
[23]
Table 1. Mechanical properties of natural blood vessel and artificial blood vessel
Mechanical properties Natural blood vessel Artificial blood vessel
Burst pressure 3775 mmHg 1000 mmHg
Tensile strength 0.2–0.6 MPa to 2–6 MPa >1 MPa
Diameter 18–24 mm (thoracic endovascular aortic repair); 6–10 mm (other blood vessel)
Suture retention Yes Yes
Kink and compression resistance Yes Yes
Maintenance of a functional endothelium Yes Yes
Low manufacturing costs Yes
Easy storage Yes
[34]
2.2. Hydrogel requirements material and is related to viscous flow . An increase
The main properties of the hydrogel or bioink include in the viscosity of hydrogel slows down the flow and
shear thinning, yield stress, viscosity, and molding ability deformation, thereby reducing the possibility of collapse of
that may be influenced by the embedded cell . Shear the topological structure during the primary and secondary
[29]
[35]
thinning is a phenomenon in which the viscosity decreases cross-linking . However, higher viscosity could result
with the increase of shear stress, and it is caused by the in plugging around the injection port. Changing the
untangling and orientation of polymer chain during the molecular weight and concentration of polymer, or adding
flow of polymer solution . Especially for extrusion type modifier, are some of the approaches used to enhance the
[30]
bioink, non-Newtonian fluid behavior occurs during viscosity. For example, the viscosity of 1.5% HA is about
extrusion, which increases the shear rate and reduces the 22 Pa. s, the viscosity of collagen at a concentration of
[36]
viscosity . During the printing process, bioink must shift 1.5 – 1.75% is around 1.7 – 1.8 Pa·s . Taken together, the
[31]
from high-viscosity gel to low-viscosity fluid, and then, the influence of viscosity on the performance of bioink should
[37]
internal structure is quickly renewed, thereby improving be considered comprehensively .
the viscosity to maintain the structural integrity . Thus, In addition to meet the basic rheological properties and
[32]
the basic of shear thinning is proper viscosity behavior, mechanical properties, the cellular compatibility of the
[38]
which is usually described in terms of storage (or elastic) hydrogels also needs to balance during preparation . The
modulus G’ and loss (or viscous) modulus G” . The bioink is the only environment that supports and provides
[33]
loss modulus G” measures the energy dissipated by a nutrition to the cells; on the contrary, the existence of the
Volume 9 Issue 4 (2023) 411 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.740