Page 287 - IJB-9-5
P. 287
International Journal of Bioprinting Blood components for tissue graft bioprinting
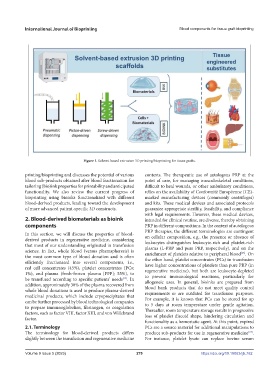
Figure 1. Solvent-based extrusion 3D printing/bioprinting for tissue grafts.
printing/bioprinting and discusses the potential of various contexts. The therapeutic use of autologous PRP at the
blood sub-products obtained after blood fractionation for point of care, for managing musculoskeletal conditions,
tailoring (bio)ink properties for printability and anticipated difficult to heal wounds, or other ambulatory conditions,
functionality. We also review the current progress of relies on the availability of Conformité Européenne (CE)-
bioprinting using bioinks functionalized with different marked manufacturing devices (commonly centrifuges)
blood-derived products, leading toward the development and kits. These medical devices and associated protocols
of more advanced patient-specific 3D constructs. guarantee appropriate sterility, feasibility, and compliance
with legal requirements. However, these medical devices,
2. Blood-derived biomaterials as bioink intended for clinical routine, are diverse, thereby obtaining
components PRP in different compositions. In the context of autologous
PRP therapies, the different terminologies are contingent
In this section, we will discuss the properties of blood- on cellular composition, e.g., the presence or absence of
derived products in regenerative medicine, considering leukocytes distinguishes leukocyte-rich and platelet-rich
that most of our understanding originated in transfusion plasma (L-PRP and pure PRP, respectively), and on the
science. In fact, whole blood (versus plasmapheresis) is enrichment of platelets relative to peripheral blood . On
[23]
the most common type of blood donation and is often the other hand, platelet concentrates (PCs) in transfusion
efficiently fractionated into several components, i.e., have higher concentrations of platelets than pure PRP (in
red cell concentrates (45%), platelet concentrates (PCs; regenerative medicine), but both are leukocyte-depleted
1%), and plasma (fresh-frozen plasma [FFP]; 55%), to to prevent immunological reactions, particularly for
be transfused according to specific patients’ needs . In allogeneic uses. In general, bioinks are prepared from
[22]
addition, approximately 30% of the plasma recovered from blood bank products that do not meet quality control
whole blood donations is used to produce plasma-derived requirements or are outdated for transfusion purposes.
medicinal products, which include cryoprecipitates that For example, it is known that PCs can be stored for up
can be further processed by blood technological companies to 5 days at room temperature under gentle agitation.
to prepare immunoglobulins, fibrinogen, or coagulation Thereafter, room temperature storage results in progressive
factors, such as factor VIII, factor XIII, and von Willebrand loss of platelet discoid shape, hindering circulation and
factor.
functionality as a hemostatic agent. At this point, expired
2.1. Terminology PCs are a source material for additional manipulations to
The terminology for blood-derived products differs produce sub-products for use in regenerative medicine .
[24]
slightly between the transfusion and regenerative medicine For instance, platelet lysate can replace bovine serum
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 279 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.762