Page 405 - IJB-9-5
P. 405
International Journal of Bioprinting A sturgeon cartilage extracellular matrix-derived bioactive bioink
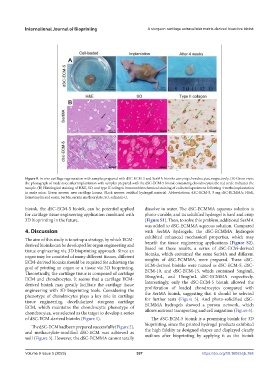
Figure 9. In vivo cartilage regeneration with samples prepared with dSC-ECM-5 and SerMA bioinks carrying chondrocytes, respectively. (A) Gross view;
the photograph of nude mice after implantation with samples prepared with the dSC-ECM-5 bioink containing chondrocytes; the red circle indicates the
sample. (B) Histological staining of H&E, SO, and type II collagen immunohistochemical staining of collected specimens following 4 weeks implantation
in nude mice. Green arrows: new cartilage lacuna. Black arrows: residual hydrogel material. Abbreviations: dSC-ECM-5, 5 mg dSC-ECMMA; H&E,
hematoxylin and eosin; SerMa, sericin methacrylate; SO, safranin-O.
bioink, the dSC-ECM-5 bioink, can be potential applied dissolve in water. The dSC-ECMMA aqueous solution is
for cartilage tissue engineering application combined with photo-curable, and its solidified hydrogel is hard and crisp
3D bioprinting in the future. (Figure S1). Then, to solve this problem, additional SerMA
was added to dSC-ECMMA aqueous solution. Compared
4. Discussion with SerMA hydrogels, the dSC-ECMMA hydrogels
exhibited enhanced mechanical properties, which may
The aim of this study is to set up a strategy, by which ECM-
derived bioinks can be developed for organ engineering and benefit the tissue engineering applications (Figure S2).
tissue engineering via 3D bioprinting approach. Since an Based on these results, a series of dSC-ECM-derived
organ may be consisted of many different tissues, different bioinks, which contained the same SerMA and different
ECM-derived bioinks should be required for achieving the weights of dSC-ECMMA, were prepared. These dSC-
goal of printing an organ or a tissue via 3D bioprinting. ECM-derived bioinks were named as dSC-ECM-5, dSC-
Theoretically, the cartilage tissue is composed of cartilage ECM-10, and dSC-ECM-15, which contained 5mg/mL,
ECM and chondrocytes. It seems that a cartilage ECM- 10mg/mL, and 15mg/mL dSC-ECMMA respectively.
derived bioink may greatly facilitate the cartilage tissue Interestingly, only the dSC-ECM-5 bioink allowed the
engineering with 3D bioprinting tools. Considering the proliferation of loaded chondrocytes compared with
phenotype of chondrocytes plays a key role in cartilage the SerMA bioink, suggesting that it should be selected
tissue engineering, decellularized sturgeon cartilage for further tests (Figure 5). And photo-solidified dSC-
ECM, which maintains the chondrocytic phenotype of ECMMA hydrogels showed a porous network, which
chondrocytes, was selected as the target to develop a series allows nutrient transporting and cell migration (Figure 6).
of dSC-ECM-derived bioinks (Figure 1). The dSC-ECM-5 bioink is a promising bioink for 3D
bioprinting, since the printed hydrogel products exhibited
The dSC-ECM had been prepared successfully (Figure 2),
and methacrylate-modified dSC-ECM was achieved as the high fidelity as designed shapes and displayed clearly
outlines after bioprinting by applying it as the bioink
well (Figure 3). However, the dSC-ECMMA cannot totally
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 397 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.768