Page 209 - IJB-9-6
P. 209
International Journal of Bioprinting Multi-Cellular tissues/organoids manufacturing strategies
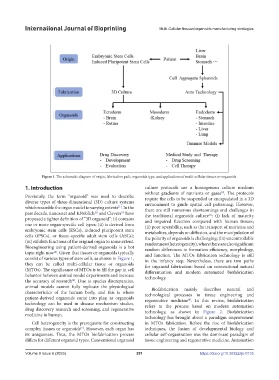
Figure 1. The schematic diagram of origin, fabrication path, organoids type, and applications of multi-cellular tissues or organoids.
1. Introduction culture protocols use a homogenous culture medium
without gradients of nutrients or gases . The protocols
[6]
Previously, the term “organoid” was used to describe require the cells to be suspended or encapsulated in a 3D
diverse types of three-dimensional (3D) culture systems environment to guide spatial cell patterning. However,
which resemble the organ model to varying extents . In the there are still numerous shortcomings and challenges in
[1]
past decade, Lancaster and KNoblich and Clevers have the traditional organoids culture : (i) lack of maturity
[3]
[2]
[7]
proposed a tighter definition of “3D organoid”: (i) contains and impaired function compared with human tissues;
one or more organ-specific cell types; (ii) is derived from (ii) poor operability, such as the transport of nutrients and
embryonic stem cells (ESCs), induced pluripotent stem metabolites, depends on diffusion, and the manipulation of
cells (iPSCs), or tissue-specific adult stem cells (ASCs); the polarity of organoids is challenging; (iii) uncontrollable
(iii) exhibits functions of the original organ to some extent. randomness (heterogeneity), where there are also significant
Bioengineering using patient-derived organoids is a hot random differences in formation efficiency, morphology,
topic right now . Given that tissues or organoids typically and function. The MTOs fabrication technology is still
[4]
consist of various types of stem cells, as shown in Figure 1, in the infancy step. Nevertheless, there are two paths
they can be called multi-cellular tissue or organoids for organoid fabrication: based on conventional natural
(MTOs). The significance of MTOs is to fill the gap in cell differentiation and modern automated biofabrication
behavior between animal model experiments and increase technology.
the accuracy of research . Due to species discrepancies,
[4]
animal models cannot fully replicate the physiological Biofabrication mainly describes natural and
characteristics of the human body, and this is where technological processes in tissue engineering and
patient-derived organoids come into play, as organoids regenerative medicine . In this review, biofabrication
[8]
technology can be used in disease mechanism studies, refers to the process based on modern automation
drug discovery research and screening, and regenerative technology, as shown in Figure 2. Biofabrication
medicine in human.
technology has brought about a paradigm improvement
Cell heterogeneity is the prerequisite for constructing in MTOs fabrication. Before the rise of biofabrication
complex tissues or organoids . However, each organ has techniques, the fusion of developmental biology and
[5]
its uniqueness. Thus, the MTOs biofabrication process cellular self-organization was the dominant paradigm of
differs for different organoid types. Conventional organoid tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Automation
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 201 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0135