Page 318 - IJB-9-6
P. 318
International Journal of Bioprinting Rheology-informed machine learning model
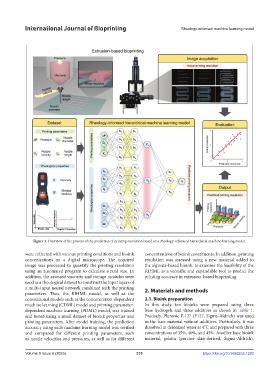
Figure 1. Overview of the process of the prediction of printing resolution based on a rheology-informed hierarchical machine learning model.
were collected with various printing conditions and bioink concentrations of bioink constituents. In addition, printing
concentrations on a digital microscope. The acquired resolution was assessed using a new material added to
image was processed to quantify the printing resolution the alginate-based bioink, to examine the feasibility of the
using an automated program to calculate strand size. In RIHML as a versatile and expandable tool to predict the
addition, the assessed viscosity and storage modulus were printing accuracy in extrusion-based bioprinting.
used as a rheological dataset to construct the input layers of
a multi-input neural network combined with the printing 2. Materials and methods
parameters. Thus, the RIHML model, as well as the
conventional models such as the concentration-dependent 2.1. Bioink preparation
machine learning (CDML) model and printing parameter- In this study, ten bioinks were prepared using three
dependent machine learning (PDML) model, was trained base hydrogels and three additives as shown in Table 1.
and tested using a small dataset of bioink properties and Precisely, Pluronic F-127 (F127, Sigma-Aldrich) was used
printing parameters. After model training, the prediction as the base material without additives. Particularly, it was
accuracy using each machine learning model was verified dissolved in deionized water at 4°C and prepared with three
and compared for different printing parameters, such concentrations of 35%, 40%, and 45%. Another base bioink
as nozzle velocities and pressures, as well as for different material, gelatin (porcine skin-derived, Sigma-Aldrich),
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 310 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.1280