Page 323 - IJB-9-6
P. 323
International Journal of Bioprinting Rheology-informed machine learning model
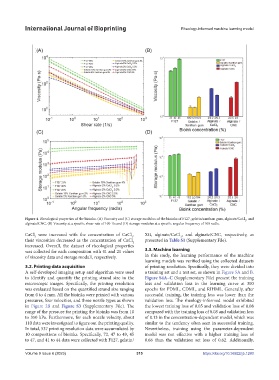
Figure 4. Rheological properties of the bioinks. (A) Viscosity and (C) storage modulus of the bioinks of F127, gelatin/xanthan gum, alginate/CaCl , and
2
alginate/CNC. (B) Viscosity at a specific shear rate of 100 1/s and (D) storage modulus at a specific angular frequency of 100 rad/s.
CaCl were increased with the concentration of CaCl , XG, alginate/CaCl , and alginate/CNC, respectively, as
2
2
2
their viscosities decreased as the concentration of CaCl presented in Table S1 (Supplementary File).
2
increased. Overall, the dataset of rheological properties
was collected for each composition with 41 and 21 values 3.3. Machine learning
of viscosity data and storage moduli, respectively. In this study, the learning performance of the machine
learning models was verified using the collected datasets
3.2. Printing data acquisition of printing resolution. Specifically, they were divided into
A self-developed imaging setup and algorithm were used a training set and a test set, as shown in Figure 5A and B.
to identify and quantify the printing strand size in the Figure S4A–C (Supplementary File) present the training
microscopic images. Specifically, the printing resolution loss and validation loss in the learning curve at 300
was evaluated based on the quantified strand size ranging epochs for PDML, CDML, and RIHML. Generally, after
from 0 to 4 mm. All the bioinks were printed with various successful training, the training loss was lower than the
pressures, four velocities, and three nozzle types as shown validation loss. The rheology-informed model exhibited
in Figure 2B and Figure S3 (Supplementary File). The the lowest training loss of 0.05 and validation loss of 0.08
range of the pressure for printing the bioinks was from 10 compared with the training loss of 0.08 and validation loss
to 350 kPa. Furthermore, for each nozzle velocity, about of 0.13 in the concentration-dependent model, which was
110 data were investigated to figure out the printing quality. similar to the tendency often seen in successful training.
In total, 537 printing resolution data were accumulated by Nevertheless, training using the parameter-dependent
10 compositions of bioinks. Specifically, 72, 47 to 49, 45 model was not effective with a higher training loss of
to 47, and 41 to 44 data were collected with F127, gelatin/ 0.68 than the validation set loss of 0.62. Additionally,
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 315 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.1280