Page 325 - IJB-9-6
P. 325
International Journal of Bioprinting Rheology-informed machine learning model
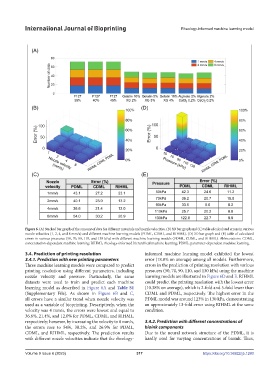
Figure 6. (A) Stacked bar graph of the amount of data for different materials and nozzle velocities. (B) 3D bar graph and (C) table of calculated errors in various
nozzle velocities (1, 2, 4, and 8 mm/s) and different machine learning models (PDML, CDML, and RIHML). (D) 3D bar graph and (E) table of calculated
errors in various pressures (50, 70, 90, 110, and 130 kPa) with different machine learning models (PDML, CDML, and RIHML). Abbreviations: CDML,
concentration-dependent machine learning; RIHML, rheology-informed hierarchical machine learning; PDML, parameter-dependent machine learning.
3.4. Prediction of printing resolution informed machine learning model exhibited the lowest
3.4.1. Prediction with new printing parameters error (18.8% on average) among all models. Furthermore,
Three machine learning models were compared to predict errors in the prediction of printing resolution with various
printing resolution using different parameters, including pressures (50, 70, 90, 110, and 130 kPa) using the machine
nozzle velocity and pressure. Particularly, the same learning models are illustrated in Figure 6D and E. RIHML
datasets were used to train and predict each machine could predict the printing resolution with the lowest error
learning model as described in Figure 6A and Table S1 (10.38% on average), which is 2-fold and 5-fold lower than
(Supplementary File). As shown in Figure 6B and C, CDML and PDML, respectively. The highest error in the
all errors have a similar trend when nozzle velocity was PDML model was around 123% in 130 kPa, demonstrating
used as a variable of bioprinting. Descriptively, when the an approximately 13-fold error using RIHML at the same
velocity was 4 mm/s, the errors were lowest and equal to condition.
36.6%, 21.4%, and 12.0% for PDML, CDML, and RIHML,
respectively; however, by increasing the velocity to 8 mm/s, 3.4.2. Prediction with different concentrations of
the errors rose to 54%, 30.2%, and 26.9% for PDML, bioink components
CDML, and RIHML, respectively. The prediction results Due to the neural network structure of the PDML, it is
with different nozzle velocities indicate that the rheology- hardly used for varying concentrations of bioink. Thus,
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 317 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.1280