Page 435 - IJB-9-6
P. 435
International Journal of Bioprinting Versatile pomelo peel-inspired structures
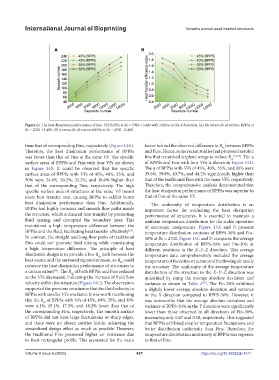
Figure 11. The heat dissipation performance of four VFs BPPSs at Re = 2700–13,400 with airflow in the X direction. (A) Nu versus Re of various BPPSs at
Re = 2700–13,400. (B) η versus Re of various BPPSs at Re = 2700–13,400.
than that of corresponding Fins, respectively (Figure 14A). factor behind the observed difference in R between BPPSs
th
Therefore, the heat dissipation performance of BPPSs and Fins. Hence, some recent studies had proposed aerofoil
was better than that of Fins at the same VF. The specific fins that mimicked airplane wings to reduce R th [63,64] . The η
surface areas of BPPSs and Fins with four VFs are shown of BPPSs and Fins with four VFs is shown in Figure 14D.
in Figure 14B. It could be observed that the specific The η of BPPSs with VFs of 45%, 40%, 35%, and 30% were
surface areas of BPPSs with VFs of 45%, 40%, 35%, and 39.6%, 39.8%, 43.7%, and 44.2% significantly higher than
30% were 24.4%, 30.2%, 32.2%, and 38.6% higher than that of the traditional Fins with the same VFs, respectively.
that of the corresponding Fins, respectively. The high Therefore, the comprehensive analysis demonstrated that
specific surface area of structures at the same VF meant the heat dissipation performance of BPPSs was superior to
more heat transfer area, causing BPPSs to exhibit better that of Fins at the same VF.
heat dissipation performance than Fins. Additionally, The uniformity of temperature distribution is an
BPPSs had highly tortuous and smooth flow paths inside important factor for evaluating the heat dissipation
the structure, which enhanced heat transfer by promoting performance of structures. It is essential to maintain a
fluid mixing, and disrupted the boundary layer. This uniform temperature distribution for the stable operation
maintained a high temperature difference between the of electronic components. Figure 15A and B presents
BPPSs and the fluid, facilitating heat transfer effectively . temperature distribution contours of BPPS-30% and Fin-
[65]
In contrast, the straight and long flow paths of traditional 30% at Re = 2700. Figure 15C and D compares the average
Fins could not promote fluid mixing while maintaining temperature distribution of BPPS-30% and Fin-30% at
a high temperature difference. The principle of heat different positions in the X–Y–Z direction. This average
dissipation design is to provide a low R path between the temperature data comprehensively included the average
th
heat source and the surrounding environment, so R could temperature of the entire structure and the flowing air inside
th
measure the heat dissipation performance of structures to the structure. The uniformity of the average temperature
a certain extent . The R of both BPPSs and Fins reduced distribution of the structure in the X–Y–Z direction was
[44]
th
as the VFs decreased, indicating the increase of fluid flow quantified by using the average absolute deviation and
velocity within the structure (Figure 14C). The observation variance as shown in Table 4 . The Fin-30% exhibited
[66]
supported the previous conclusion that the fluid velocity in a slightly lower average absolute deviation and variance
BPPSs with smaller VFs was faster. It was worth mentioning in the X direction compared to BPPS-30%. However, it
that the R of BPPSs with VFs of 45%, 40%, 35%, and 30% was noteworthy that the average absolute deviation and
th
were 4.1%, 15.1%, 17.3%, and 18.2% lower than that of variance of BPPS-30% in the Y direction were significantly
the corresponding Fins, respectively. The smooth surface lower than those observed in all directions of Fin-30%,
of BPPSs did not have large fluctuations or sharp edges, measuring only 0.67 and 0.58, respectively. This suggested
and there were no closed cavities inside, achieving the that BPPSs exhibited smaller temperature fluctuations and
streamlined design effect as much as possible. However, better distribution uniformity than Fins. Therefore, the
the traditional Fins possessed higher air resistance due temperature distribution uniformity of BPPSs was superior
to their rectangular profile. This accounted for the main to that of Fins.
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 427 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.1011