Page 515 - IJB-9-6
P. 515
International Journal of Bioprinting Advances for 3D-printed oral drug delivery systems
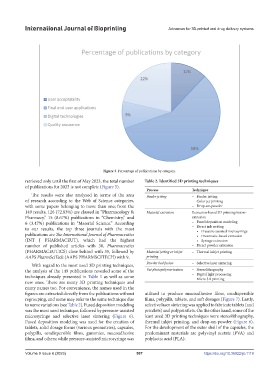
Figure 3. Percentage of publications by category.
retrieved only until the first of May 2023, the total number Table 2. Identified 3D printing techniques
of publications for 2023 is not complete (Figure 5).
Process Technique
The results were also analyzed in terms of the area Binder jetting – Binder jetting
of research according to the Web of Science categories, – Color jet printing
with some papers belonging to more than one; from the – Drop-on-powder
149 results, 126 (72.83%) are classed in “Pharmacology & Material extrusion Extrusion-based 3D printing/micro-
Pharmacy,” 15 (8.67%) publications in “Chemistry,” and extrusion
6 (3.47%) publications in “Material Science.” According – Fused deposition modeling
to our results, the top three journals with the most – Direct ink writing
• Pressure-assisted microsyringe
publications are The International Journal of Pharmaceutics • Pneumatic-based extrusion
(INT J PHARMACEUT), which had the highest • Syringe extrusion
number of published articles with 38, Pharmaceutics – Direct powder extrusion
(PHARMACEUTICS) close behind with 35, followed by Material jetting or inkjet – Thermal inkjet printing
AAPS PharmSciTech (AAPS PHARMSCITECH) with 9. printing
With regard to the most used 3D printing techniques, Powder bed fusion – Selective laser sintering
the analysis of the 149 publications revealed some of the Vat photopolymerization – Stereolithography
techniques already presented in Table 1 as well as some – Digital light processing
– Micro 3D printing
new ones. There are many 3D printing techniques and
many names too. For convenience, the names used in the
figures are extracted directly from the publications without utilized to produce mucoadhesive films, orodispersible
regrouping, and some may refer to the same technique due films, polypills, tablets, and soft dosages (Figure 7). Lastly,
to name variations (see Table 2). Fused deposition modeling selective laser sintering was applied to fabricate tablets (and
was the most used technique, followed by pressure-assisted printlets) and polyprintlets. On the other hand, some of the
microsyringe and selective laser sintering (Figure 6). least used 3D printing techniques were stereolithography,
Fused deposition modeling was used for the creation of thermal inkjet printing, and drop-on-powder (Figure 6).
tablets, solid dosage forms (various geometries), capsules, For the development of the outer shell of the capsules, the
polypills, orodispersible films, gummies, mucoadhesive predominant materials are polyvinyl acetate (PVA) and
films, and others; while pressure-assisted microsyringe was polylactic acid (PLA).
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 507 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.1119