Page 41 - v11i4
P. 41
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D bioprinting of nerve guidance conduits
injury repair process and formulating effective intervention length is longer, it is difficult for regenerated nerve axons
strategies. Nerves are composed of numerous axons that are to accurately bridge the proximal-distal ends of the
wrapped and supported by connective tissues, including defective nerves. Consequently, the nerve’s self-repair
6
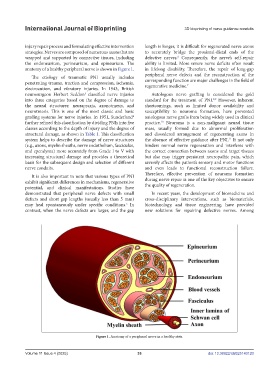
the endoneurium, perineurium, and epineurium. The ability is limited. More severe nerve deficits often result
anatomy of a healthy peripheral nerve is shown in Figure 1. in lifelong disability. Therefore, the repair of long-gap
peripheral nerve defects and the reconstruction of the
The etiology of traumatic PNI usually includes
penetrating trauma, traction and compression, ischemia, corresponding function are major challenges in the field of
regenerative medicine.
7
electrocution, and vibratory injuries. In 1943, British
neurosurgeon Herbert Seddon classified nerve injuries Autologous nerve grafting is considered the gold
3
into three categories based on the degree of damage to standard for the treatment of PNI. However, inherent
8,9
the neural structures: neurapraxia, axonotmesis, and shortcomings, such as limited donor availability and
neurotmesis. This is one of the most classic and basic susceptibility to neuroma formation, have prevented
grading systems for nerve injuries. In 1951, Sunderland autologous nerve grafts from being widely used in clinical
4
further refined this classification by dividing PNIs into five practice. Neuroma is a non-malignant neural tissue
10
classes according to the depth of injury and the degree of mass, usually formed due to abnormal proliferation
structural damage, as shown in Table 1. This classification and disordered arrangement of regenerating axons in
system helps to describe the damage of nerve structures the absence of effective guidance after PNI. It not only
11
(e.g., axons, myelin sheaths, nerve endothelium, fasciculus, hinders normal nerve regeneration and interferes with
and ependyma) more accurately from Grade I to V with the correct connection between axons and target tissues
increasing structural damage and provides a theoretical but also may trigger persistent neuropathic pain, which
basis for the subsequent design and selection of different severely affects the patient’s sensory and motor functions
nerve conduits. and even leads to functional reconstruction failure.
Therefore, effective prevention of neuroma formation
It is also important to note that various types of PNI
exhibit significant differences in mechanisms, regenerative during nerve repair is one of the key objectives to ensure
potential, and clinical manifestations. Studies have the quality of regeneration.
demonstrated that peripheral nerve defects with small In recent years, the development of biomedicine and
defects and short gap lengths (usually less than 5 mm) cross-disciplinary interventions, such as biomaterials,
may heal spontaneously under specific conditions. In biotechnology, and tissue engineering, have provided
5
contrast, when the nerve defects are larger, and the gap new solutions for repairing defective nerves. Among
Figure 1. Anatomy of a peripheral nerve in a healthy state.
Volume 11 Issue 4 (2025) 33 doi: 10.36922/IJB025140120