Page 20 - IJOCTA-15-3
P. 20
A. Kaveh, M. Vahedi, M. Gandomkar / IJOCTA, Vol.15, No.3, pp.379-395 (2025)
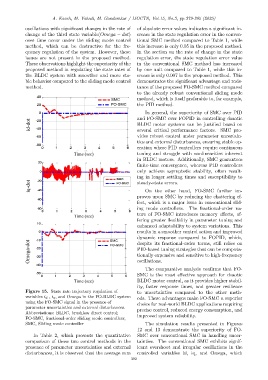
oscillations with significant changes in the rate of of absolute error values indicates a significant in-
change of the third state variable(Omega − dot) crease in the state regulation error in the conven-
over time occur under the sliding mode control tional SMC method compared to Table 1, while
method, which can be destructive for the fre- this increase is only 0.05 in the proposed method.
quency regulation of the system. However, these In the section on the rate of change in the state
issues are not present in the proposed method. regulation error, the state regulation error value
These observations highlight the superiority of the in the conventional SMC method has increased
proposed method in regulating the state rates of by one unit compared to Table 1, while this in-
the BLDC system with smoother and more sta- crease is only 0.007 in the proposed method. This
ble behavior compared to the sliding mode control demonstrates the significant advantage and resis-
method. tance of the proposed FO-SMC method compared
to the already robust conventional sliding mode
method, which is itself preferable to, for example,
the PID method.
In general, the superiority of SMC over PID
and FO-SMC over FOPID in controlling chaotic
BLDC motor systems can be justified based on
several critical performance factors. SMC pro-
vides robust control under parameter uncertain-
ties and external disturbances, ensuring stable op-
eration where PID controllers require continuous
tuning and struggle with nonlinearities inherent
in BLDC motors. Additionally, SMC guarantees
finite-time convergence, whereas PID controllers
only achieve asymptotic stability, often result-
ing in longer settling times and susceptibility to
steady-state errors.
On the other hand, FO-SMC further im-
proves upon SMC by reducing the chattering ef-
fect, which is a major issue in conventional slid-
ing mode controllers. The fractional-order na-
ture of FO-SMC introduces memory effects, of-
fering greater flexibility in parameter tuning and
enhanced adaptability to system variations. This
results in a smoother control action and improved
dynamic response compared to FOPID, which,
despite its fractional-order terms, still relies on
PID-based tuning strategies that can be computa-
tionally expensive and sensitive to high-frequency
oscillations.
The comparative analysis confirms that FO-
SMC is the most effective approach for chaotic
BLDC motor control, as it provides higher stabil-
ity, faster response times, and greater resilience
Figure 15. State rate trajectory regulation of to uncertainties compared to the other meth-
variables i d , i q , and Omega in the FO-BLDC system ods. These advantages make FO-SMC a superior
using the FO-SMC signal in the presence of choice for real-world BLDC applications requiring
parameter uncertainties and external disturbances. precise control, reduced energy consumption, and
Abbreviations: BLDC, brushless direct control; improved system reliability.
FO-SMC, fractional-order sliding mode controllers;
SMC, Sliding mode controller The simulation results presented in Figures
12 and 13 demonstrate the superiority of FO-
In Table 2, which presents the quantitative SMC over conventional SMC in handling uncer-
comparison of these two control methods in the tainties. The conventional SMC exhibits signif-
presence of parameter uncertainties and external icant overshoot and irregular oscillations in the
disturbances, it is observed that the average sum controlled variables id, iq, and Omega, which
392