Page 17 - IJOCTA-15-3
P. 17
Improving the performance of a chaotic nonlinear system of fractional-order...
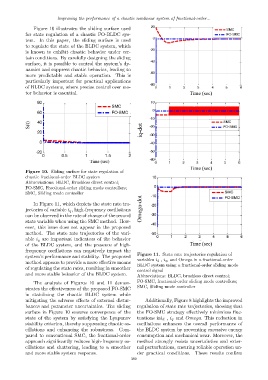
Figure 10 illustrates the sliding surface used
for state regulation of a chaotic FO-BLDC sys-
tem. In this paper, the sliding surface is used
to regulate the state of the BLDC system, which
is known to exhibit chaotic behavior under cer-
tain conditions. By carefully designing the sliding
surface, it is possible to control the system’s dy-
namics and suppress chaotic behavior, leading to
more predictable and stable operation. This is
particularly important for practical applications
of BLDC systems, where precise control over mo-
tor behavior is essential.
Figure 10. Sliding surface for state regulation of
chaotic fractional-order BLDC system
Abbreviations: BLDC, Brushless direct control;
FO-SMC, Fractional-order sliding mode controllers;
SMC, Sliding mode controller
In Figure 11, which depicts the state rate tra-
jectories of variable i q , high-frequency oscillations
can be observed in the rate of change of the second
state variable when using the SMC method. How-
ever, this issue does not appear in the proposed
method. The state rate trajectories of the vari-
able i q are important indicators of the behavior
of the BLDC system, and the presence of high-
frequency oscillations can negatively impact the
Figure 11. State rate trajectories regulation of
system’s performance and stability. The proposed
variables i d , i q , and Omega in a fractional-order
method appears to provide a more effective means
BLDC system using a fractional-order sliding mode
of regulating the state rates, resulting in smoother
control signal
and more stable behavior of the BLDC system.
Abbreviations: BLDC, brushless direct control;
The analysis of Figures 10 and 11 demon- FO-SMC, fractional-order sliding mode controllers;
SMC, Sliding mode controller
strates the effectiveness of the proposed FO-SMC
in stabilizing the chaotic BLDC system while
mitigating the adverse effects of external distur- Additionally, Figure 8 highlights the improved
bances and parameter uncertainties. The sliding regulation of state rate trajectories, showing that
surface in Figure 10 ensures convergence of the the FO-SMC strategy effectively minimizes fluc-
state of the system by satisfying the Lyapunov tuations ini d , i q and Omega. This reduction in
stability criterion, thereby suppressing chaotic os- oscillations enhances the overall performance of
cillations and enhancing the robustness. Com- the BLDC system by preventing excessive energy
pared to conventional SMC, the fractional-order consumption and mechanical wear. Moreover, the
approach significantly reduces high-frequency os- method strongly resists uncertainties and exter-
cillations and chattering, leading to a smoother nal perturbations, ensuring reliable operation un-
and more stable system response. der practical conditions. These results confirm
389