Page 19 - IJOCTA-15-3
P. 19
Improving the performance of a chaotic nonlinear system of fractional-order...
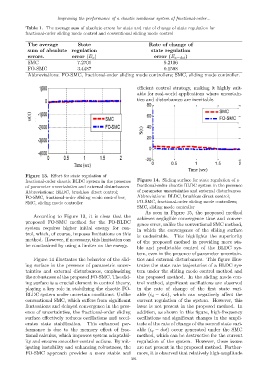
Table 1. The average sum of absolute errors for state and rate of change of state regulation for
fractional-order sliding mode control and conventional sliding mode control
The average State Rate of change of
sum of absolute regulation state regulation
errors. error (E x ) error (E x−dot )
SMC 7.2701 9.2106
FO-SMC 3.4487 0.1598
Abbreviations: FO-SMC, fractional-order sliding mode controllers; SMC, sliding mode controller.
efficient control strategy, making it highly suit-
able for real-world applications where uncertain-
ties and disturbances are inevitable.
Figure 13. Effort for state regulation of
fractional-order chaotic BLDC system in the presence Figure 14. Sliding surface for state regulation of a
of parameter uncertainties and external disturbances fractional-order chaotic BLDC system in the presence
Abbreviations: BLDC, brushless direct control; of parameter uncertainties and external disturbances
FO-SMC, fractional-order sliding mode controllers; Abbreviations: BLDC, brushless direct control;
SMC, sliding mode controller FO-SMC, fractional-order sliding mode controllers;
SMC, sliding mode controller
As seen in Figure 15, the proposed method
According to Figure 13, it is clear that the
achieves negligible convergence time and conver-
proposed FO-SMC method for the FO-BLDC
gence error, unlike the conventional SMC method,
system requires higher initial energy for con-
in which the convergence of the sliding surface
trol, which, of course, imposes limitations on this
is undesirable. This highlights the superiority
method. However, if necessary, this limitation can
of the proposed method in providing more sta-
be constrained by using a limiter on the energy.
ble and predictable control of the BLDC sys-
tem, even in the presence of parameter uncertain-
Figure 14 illustrates the behavior of the slid- ties and external disturbances. This figure illus-
ing surface in the presence of parametric uncer- trates the state rate trajectories of a BLDC sys-
tainties and external disturbances, emphasizing tem under the sliding mode control method and
the robustness of the proposed FO-SMC. The slid- the proposed method. In the sliding mode con-
ing surface is a crucial element in control theory, trol method, significant oscillations are observed
playing a key role in stabilizing the chaotic FO- in the rate of change of the first state vari-
BLDC system under uncertain conditions. Unlike able (i d − dot), which can negatively affect the
conventional SMC, which suffers from significant current regulation of the system. However, this
fluctuations and delayed convergence in the pres- issue is not present in the proposed method. In
ence of uncertainties, the fractional-order sliding addition, as shown in this figure, high-frequency
surface effectively reduces oscillations and accel- oscillations and significant changes in the ampli-
erates state stabilization. This enhanced per- tude of the rate of change of the second state vari-
formance is due to the memory effect of frac- able (i q − dot) occur generated under the SMC
tional calculus, which improves system adaptabil- method, which can be destructive for the current
ity and ensures smoother control actions. By mit- regulation of the system. However, these issues
igating instability and enhancing robustness, the are not present in the proposed method. Further-
FO-SMC approach provides a more stable and more, it is observed that relatively high-amplitude
391