Page 16 - IJOCTA-15-3
P. 16
A. Kaveh, M. Vahedi, M. Gandomkar / IJOCTA, Vol.15, No.3, pp.379-395 (2025)
performance, while the proposed method is com-
pletely smooth.
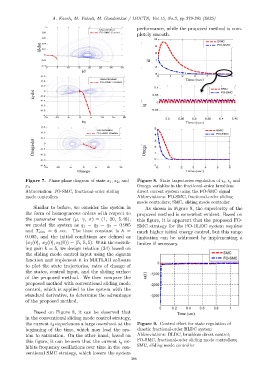
Figure 7. Phase plane diagram of state x 1 , x 2 , and Figure 8. State trajectories regulation of i d , i q and
Omega variables in the fractional-order brushless
x 3
Abbreviation: FO-SMC, fractional-order sliding direct current system using the FO-SMC signal
mode controllers Abbreviations: FO-SMC, fractional-order sliding
mode controllers; SMC, sliding mode controller
Similar to before, we consider the system in As shown in Figure 9, the superiority of the
the form of homogeneous orders with respect to proposed method is somewhat evident. Based on
the parameter vector (µ, γ, σ) = (1, 20, 5.46), this figure, it is apparent that the proposed FO-
we model the system as q 1 = q 2 = q 3 = 0.995 SMC strategy for the FO-BLDC system requires
and T sim = 6 sec. The time constant is h = much higher initial energy control, but this range
0.005, and the initial conditions are defined as limitation can be addressed by implementing a
(x 1 (0), x 2 (0), x 3 (0)) = (5, 5, 5). With the switch- limiter if necessary.
ing gain k = 5, we design relation (34) based on
the sliding mode control input using the signum
function and implement it in MATLAB software
to plot the state trajectories, rates of change of
the states, control input, and the sliding surface
of the proposed method. We then compare the
proposed method with conventional sliding mode
control, which is applied to the system with the
standard derivative, to determine the advantages
of the proposed method.
Based on Figure 8, it can be observed that
in the conventional sliding mode control strategy,
the current i d experiences a large overshoot at the Figure 9. Control effort for state regulation of
beginning of the time, which may lead the sys- chaotic fractional-order BLDC system
tem to saturation. On the other hand, based on Abbreviations: BLDC, brushless direct control;
this figure, it can be seen that the current i q ex- FO-SMC, fractional-order sliding mode controllers;
SMC, sliding mode controller
hibits frequency oscillations over time in the con-
ventional SMC strategy, which lowers the system
388