Page 117 - IJOCTA-15-4
P. 117
Rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on GJO–VMD, multiscale fuzzy entropy, and GSABO–BP...
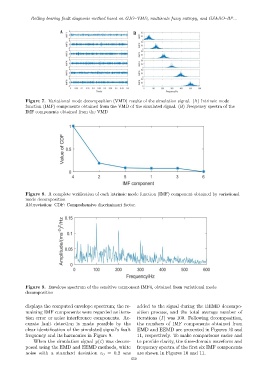
Figure 7. Variational mode decomposition (VMD) results of the simulation signal. (A) Intrinsic mode
function (IMF) components obtained from the VMD of the simulated signal. (B) Frequency spectra of the
IMF components obtained from the VMD
Figure 8. A complete verification of each intrinsic mode function (IMF) component obtained by variational
mode decomposition
Abbreviation: CDF: Comprehensive discriminant factor.
Figure 9. Envelope spectrum of the sensitive component IMF4, obtained from variational mode
decomposition
displays the computed envelope spectrum; the re- added to the signal during the EEMD decompo-
maining IMF components were regarded as itera- sition process, and the total average number of
tion error or noise interference components. Ac- iterations (I ) was 100. Following decomposition,
curate fault detection is made possible by the the numbers of IMF components obtained from
clear identification of the simulated signal’s fault EMD and EEMD are presented in Figures 10 and
frequency and its harmonics in Figure 9. 11, respectively. To make comparisons easier and
When the simulation signal y(t) was decom- to provide clarity, the time-domain waveform and
posed using the EMD and EEMD methods, white frequency spectra of the first six IMF components
noise with a standard deviation ε 0 = 0.2 was are shown in Figures 10 and 11.
659