Page 121 - IJOCTA-15-4
P. 121
Rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on GJO–VMD, multiscale fuzzy entropy, and GSABO–BP...
Figure 17. Fitness iteration curve for inner race fault signal
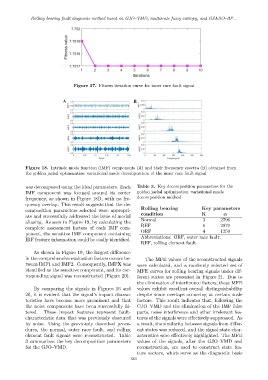
Figure 18. Intrinsic mode function (IMF) components (A) and their frequency spectra (B) obtained from
the golden jackal optimization–variational mode decomposition of the inner race fault signal
was decomposed using the ideal parameters. Each Table 3. Key decomposition parameters for the
IMF component was focused around its center golden jackal optimization–variational mode
frequency, as shown in Figure 18B, with no fre- decomposition method
quency overlap. This result suggests that the de-
Rolling bearing Key parameters
composition parameters selected were appropri-
condition K α
ate and successfully addressed the issue of modal
Normal 3 2796
aliasing. As seen in Figure 19, by calculating the
REF 6 2970
complete assessment factors of each IMF com-
ORF 4 1259
ponent, the sensitive IMF component containing
Abbreviations: ORF, outer race fault;
IRF feature information could be easily identified.
REF, rolling element fault.
As shown in Figure 19, the largest difference
in the comprehensive evaluation factors occurs be- The MFE values of the reconstructed signals
tween IMF1 and IMF2. Consequently, IMFX was were calculated, and a randomly selected set of
identified as the sensitive component, and its cor- MFE curves for rolling bearing signals under dif-
responding signal was reconstructed (Figure 20). ferent states are presented in Figure 21. Due to
the elimination of interference factors, these MFE
By comparing the signals in Figures 16 and values exhibit excellent overall distinguishability
20, it is evident that the signal’s impact charac- despite some overlaps occurring at certain scale
teristics have become more prominent and that factors. This result indicates that, following the
the noise components have been successfully fil- GJO–VMD and the elimination of the IMF false
tered. These impact features represent fault- parts, noise interference and other irrelevant fea-
characteristic data that was previously obscured tures of the signals were effectively suppressed. As
by noise. Using the previously described proce- a result, the similarity between signals from differ-
dures, the normal, outer race fault, and rolling ent states was reduced, and the signal state char-
element fault signals were reconstructed. Table acteristics were effectively highlighted. The MFE
3 summarizes the key decomposition parameters values of the signals, after the GJO–VMD and
for the GJO–VMD. reconstruction, are used to construct state fea-
ture vectors, which serve as the diagnostic basis
663