Page 85 - IJOCTA-15-4
P. 85
Advanced frequency control strategy for power systems with high renewable energy penetration
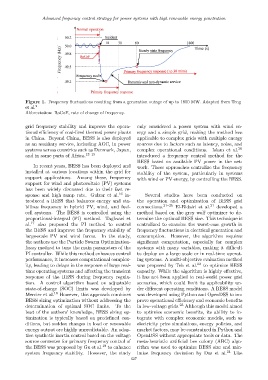
Figure 1. Frequency fluctuations resulting from a generation outage of up to 1800 MW. Adapted from Teng
et al. 2
Abbreviation: RoCoF, rate of change of frequency.
grid frequency stability and improve the opera- only considered a power system with wind en-
tional efficiency of coal-fired thermal power plants ergy and a simple grid, making the method less
in China. Beyond China, BESS is also deployed applicable to complex grids with multiple energy
as an auxiliary service, including AGC, in power sources due to factors such as latency, noise, and
systems across countries such as Denmark, Japan, complex operational conditions. Islam et al. 20
and in some parts of Africa. 13–15 introduced a frequency control method for the
BESS based on available PV power in the net-
In recent years, BESS has been deployed and work. These approaches centralize the frequency
installed at various locations within the grid for stability of the system, particularly in systems
support applications. Among these, frequency with wind or PV energy, by controlling the BESS.
support for wind and photovoltaic (PV) systems
has been widely discussed due to their fast re-
sponse and high ramp rate. Gulzar et al. 16 in- Several studies have been conducted on
troduced a BESS that balances energy and sta- the operation and optimization of BESS grid
bilizes frequency in hybrid PV, wind, and fuel- connections. 21–25 El-Bidairi et al. 21 developed a
cell systems. The BESS is controlled using the method based on the grey wolf optimizer to de-
proportional-integral (PI) method. Taghvaei et termine the optimal BESS size. This technique is
al. 17 also proposed the PI method to control centralized to examine the worst-case growth in
the BESS and improve the frequency stability of frequency fluctuations in electrical generation and
large-scale PV and wind farms. In the study, consumption. However, the algorithm requires
the authors use the Particle Swarm Optimization- significant computation, especially for complex
fuzzy method to tune the main parameters of the systems with many variables, making it difficult
PI controller. While this method enhances control to deploy on a large scale or in real-time operat-
performance, it increases computational complex- ing systems. A multi-objective evaluation method
ity, leading to delays in the response of large real- was proposed by Teh et al. 22 to optimize BESS
time operating systems and affecting the transient capacity. While the algorithm is highly effective,
response of the BESS during frequency regula- it has not been applied to real-world power grid
tion. A control algorithm based on adjustable scenarios, which could limit its applicability un-
state-of-charge (SOC) limits was developed by der different operating conditions. A BESS model
Mercier et al. 18 However, this approach combines was developed using Python and OpenDSS to im-
BESS sizing optimization without addressing the prove operational efficiency and economic benefits
determination of optimal SOC limits. To the in low-voltage grids. 23 Although this model aimed
best of the authors’ knowledge, BESS sizing op- to optimize economic benefits, its ability to in-
timization is typically based on predefined con- tegrate with complex economic models, such as
ditions, but sudden changes in load or renewable electricity price simulations, energy policies, and
energy output are highly unpredictable. An adap- market factors, may be constrained in Python and
tive synthetic inertia control based on the voltage OpenDSS without appropriate tools or data. The
source converter for primary frequency control of meta-heuristic artificial bee colony (ABC) algo-
the BESS was proposed by Gu et al. 19 to enhance rithm was used to optimize BESS size and min-
system frequency stability. However, the study imize frequency deviation by Das et al. 24 Like
627