Page 65 - IMO-2-1
P. 65
Innovative Medicines & Omics Flavonoids against glycosidic hydrolase
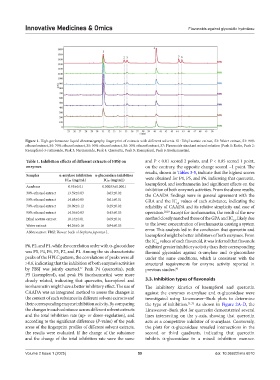
Figure 1. High-performance liquid chromatography fingerprint of extracts with different solvents. S1: Ethyl acetate extract, S2: Water extract, S3: 90%
ethanol extract, S4: 70% ethanol extract, S5: 50% ethanol extract, S6: 30% ethanol extract, S7: Flavonoids standard mixed solution (Peak 1: Rutin, Peak 2:
Kaempferol-3-rutinoside, Peak 3: Narcissoside, Peak 4: Quercetin, Peak 5: Kaempferol, Peak 6: Isorhamnetin).
Table 1. Inhibition effects of different extracts of FBSJ on and P < 0.01 scored 2 points, and P < 0.05 scored 1 point,
enzymes on the contrary, the opposite change scored −1 point. The
results, shown in Tables 3-5, indicate that the highest scores
Samples α-amylase inhibition α-glucosidase inhibition
IC50 (mg/mL) IC50 (mg/mL) were obtained for P4, P5, and P6, indicating that quercetin,
Acarbose 0.95±0.01 0.00033±0.0001 kaempferol, and isorhamnetin had significant effects on the
inhibition of both enzyme’s activities. From the above results,
30% ethanol extract 13.59±0.03 0.63±0.02 the CAADA findings were in general agreement with the
50% ethanol extract 14.68±0.05 0.61±0.01 GRA and the IC values of each substance, indicating the
50
70% ethanol extract 20.09±0.12 0.29±0.02 reliability of CAADA and its relative simplicity and ease of
90% ethanol extract 14.36±0.03 0.43±0.03 operation. 28,29 Except for isorhamnetin, the result of the new
Ethyl acetate extract 10.16±0.01 0.09±0.01 method closely matched those of the GPA and IC , likely due
50
Water extract 44.26±0.16 0.94±0.03 to the lower concentration of isorhamnetin causing a system
Abbreviation: FBSJ: Flower buds of Sophora japonica L. error. This analysis led to the conclusion that quercetin and
kaempferol might be better inhibitors of both enzymes. From
the IC values of each flavonoid, it was inferred that flavonols
50
P6, P2, and P1, while the correlation order with α-glucosidase exhibited greater inhibitory activity than their corresponding
was P5, P4, P6, P3, P2, and P1. Among the six characteristic flavonol glycosides against α-amylase and α-glucosidase
peaks of the HPLC pattern, the correlations of peaks were all under the same conditions, which is consistent with the
>0.6, indicating that the inhibition of both enzyme’s activities structural requirements for enzyme activity reported in
by FBSJ was jointly exerted. Peak P4 (quercetin), peak previous studies. 30
27
P5 (kaempferol), and peak P6 (isorhamnetin) were more
closely related, indicating that quercetin, kaempferol and 3.3. Inhibition types of flavonoids
isorhamnetin might have a better inhibitory effect. The use of The inhibitory kinetics of kaempferol and quercetin
CAADA was an integrated method to assess the changes in against the enzymes α-amylase and α-glucosidase were
the content of each substance in different solvent extracts and investigated using Lineweaver–Burk plots to determine
their corresponding enzyme inhibition activity. By comparing the type of inhibition. 31,32 As shown in Figure 2A-D, the
the changes in each substance across different solvent extracts Lineweaver–Burk plot for quercetin demonstrated several
and the total inhibition rate (up- or down-regulation), and lines intersecting on the y-axis, showing that quercetin
according to the significant difference (P-value) of the peak acts as a competitive inhibitor of α-amylase. Conversely,
areas of the fingerprint profiles of different solvent extracts, the plots for α-glucosidase revealed intersections in the
the results were evaluated. If the change of the substance second or third quadrants, indicating that quercetin
and the change of the total inhibition rate were the same inhibits α-glucosidase in a mixed inhibition manner.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 59 doi: 10.36922/imo.6010