Page 70 - IMO-2-1
P. 70
Innovative Medicines & Omics Flavonoids against glycosidic hydrolase
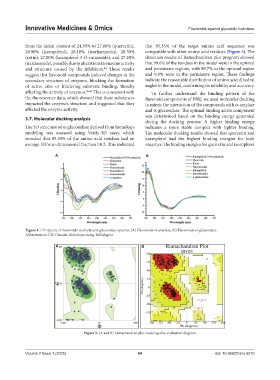
from the initial content of 24.30% to 27.00% (quercetin), that 95.35% of the target amino acid sequence was
28.90% (kaempferol), 28.10% (isorhamnetin), 28.30% compatible with other amino acid residues (Figure 5). The
(rutin), 27.00% (kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside), and 27.20% detection results of Ramachandran plot program showed
(narcissoside), possibly due to alterations in enzyme activity that 99.6% of the residues in the model were in the optimal
and structure caused by the inhibitors. These results and permissive regions, with 89.7% in the optimal region
44
suggest that flavonoid compounds induced changes in the and 9.9% were in the permissive region. These findings
secondary structure of enzymes, blocking the formation indicate the reasonable distribution of amino acid dihedral
of active sites or hindering substrate binding, thereby angles in the model, confirming its reliability and accuracy.
affecting the activity of enzymes. 45,46 This is consistent with To further understand the binding pattern of the
the fluorescence data, which showed that these substances flavonoid components of FBSJ, we used molecular docking
impacted the enzyme’s structure and suggested that they to mimic the interaction of the compounds with α-amylase
affected the enzyme activity. and α-glucosidase. The optimal binding active component
was determined based on the binding energy generated
3.7. Molecular docking analysis
during the docking process. A higher binding energy
The 3D structure of α-glucosidase derived from homology indicates a more stable complex with tighter binding.
modeling was assessed using Verify-3D assay, which The molecular docking results showed that quercetin and
revealed that 95.35% of the amino acid residues had an kaempferol had the highest binding energies for both
average 3D/one-dimensional fraction ≥0.2. This indicated enzymes. The binding energies for quercetin and kaempferol
A B
Figure 4. CD spectra of flavonoids-α-amylase/α-glucosidase systems. (A) Flavonoids-α-amylase; (B) Flavonoids-α-glucosidase.
Abbreviations: CD: Circular dichroism; mdeg: Millidegree.
A B
Figure 5. (A and B) Ramachandran plot model quality evaluation diagram
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 64 doi: 10.36922/imo.6010