Page 11 - IMO-2-3
P. 11
Innovative Medicines & Omics MSC exosomes for digestive tumors: Bench to bedside
invasion. This suggests that delivering miR-424-3p expression of aquaporin 5 (AQP5) and EGFR genes, which
through BMMSC-exo is a promising therapeutic approach are key molecules in tumor progression, within the HCT-
for GC. In addition, MSC-exo conferred drug resistance 116 tumor cell line. BMMSC-exo can also deliver miR-
41
35
to GC cells, primarily through their protein content. 100 into CRC cells, downregulating the mTOR/miR-143
These proteins activate the CaM-Ks/Raf/MEK/ERK axis and inhibiting CRC cell proliferation, migration, and
signaling pathway, increase multidrug resistance protein invasion. In addition, BMMSC-exo can inhibit tumor-
42
expression, and protect GC cells from chemotherapy- associated macrophage activity. Research has demonstrated
induced apoptosis. Another study found that exosomes that UCMSC-exo mediates miR-1827, inhibiting SUCNR1
36
from p53-deficient BMMSCs enhance the proliferation in CRC cells. Furthermore, UCMSC-exo also suppresses
and migration of GC cells and p53 wild-type BMMSCs. M2 macrophage polarization and liver metastasis. 43
37
Research has also reported that BMMSC-exo can transfer Studies have confirmed that MSC-exo significantly
miR-374a-5p to GC cells, enhancing the expression of inhibits overexpressed integrin family proteins in CRC
adhesion molecules in these cells by targeting HAPLN1, 44
which in turn facilitates the migration of GC cells. cells. Xu et al. demonstrated that integrin α2 (ITGA2)
38
BMMSC-exo has been proposed to secrete miR-221, is overexpressed in CRC cells. It is indicated that miR-
which acts as a tumor-promoting molecule by activating 16-5p derived from BMMSC-exo inhibits CRC cells by
44
the Hedgehog and PTEN/P27 signaling pathways, thereby downregulating ITGA2. Some studies have reported that
promoting GC proliferation and progression. Moreover, MSC-exo may promote CRC. AMSC-exo promotes the
39
BMMSC-exo can promote tumor growth by triggering the advancement of CRC by triggering the transformation
Hedgehog signaling pathway (Table 2). of MSCs into CAFs (MSC-CAFs) via the TRPC3/NF-KB
40
signaling pathway (Table 3).
45
3.3. Colorectal cancer (CRC) In recent years, MSC-exo-based therapies have become
For advanced-stage CRC, enhancing the efficacy of drug a key focus of research for treating CRC. Studies have
therapy is crucial. Most studies suggest that MSC-exo can reported that UCMSC-exo upregulates miR-431-5p,
inhibit CRC. AMSC-exo has been reported to suppress the consequently inhibiting CRC progression by suppressing
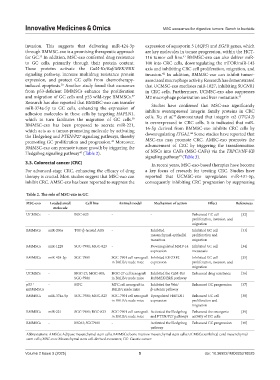
Table 2. The role of MSC‑exo in GC
MSC‑exo Loaded small Cell line Animal model Mechanism of action Effect References
molecule
UCMSCs - BGC-823 - - Enhanced GC cell [32]
proliferation, invasion, and
migration
BMMSCs miR-200a TGF-β-treated AGS - Inhibited Inhibited GC cell [33]
mesenchymal-epithelial proliferation and
transition migration
BMMSCs miR-1228 SGC-7901; MGC-823 - Downregulated MMP-14 Inhibited GC cell [34]
expression metastasis
BMMSCs miR-424-3p SGC-7901 SGC-7901 cell xenograft Inhibited RHOXF2 Inhibited GC cell [35]
in BALB/c nude mice expression proliferation, invasion, and
migration
UCMSCs - HGC-27; MGC-803; HGC-27 cell xenograft Inhibited the CaM-Ks/ Enhanced drug resistance [36]
SGC-7901 in BALB/c nude mice Raf/MEK/ERK pathway
p53 –/– - MFC MFC cell xenograft in Inhibited the Wnt/ Enhanced GC progression [37]
mBMMSCs BALB/c nude mice β-catenin pathway
BMMSCs miR-374a-5p SGC-7901; MGC-823 SGC-7901 cell xenograft Upregulated HAPLN1 Enhanced GC cell [38]
in BALB/c nude mice expression proliferation and
migration
BMMSCs miR-221 SGC-7901; BGC-823 SGC-7901 cell xenograft Activated the Hedgehog Enhanced the oncogenic [39]
in BALB/c nude mice and PTEN/P27 pathways activity of GC cells
BMMSCs - MG63; SGC7901 - Activated the Hedgehog Enhanced GC progression [40]
pathway
Abbreviations: AMSCs: Adipose mesenchymal stem cells; BMMSCs: bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; UCMSCs: umbilical cord mesenchymal
stem cells; MSC-exo: Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes; GC: Gastric cancer.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 5 doi: 10.36922/IMO025210025