Page 12 - IMO-2-3
P. 12
Innovative Medicines & Omics MSC exosomes for digestive tumors: Bench to bedside
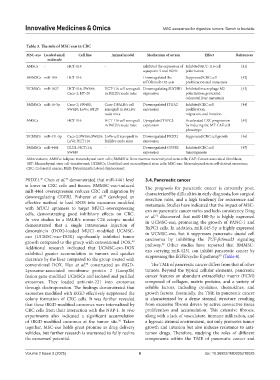
Table 3. The role of MSC‑exo in CRC
MSC‑exo Loaded small Cell line Animal model Mechanism of action Effect References
molecule
AMSCs - HCT-116 - Inhibited the expression of Inhibited HCT-116 cell [41]
aquaporin 5 and EGFR polarization
BMMSCs miR-100 HCT-116 - Downregulated the Suppressed CRC cell [42]
mTOR/miR-143 axis proliferation and metastasis
UCMSCs miR-1827 HCT-116; SW480; HCT-116 cell xenograft Downregulating SUCNR1 Inhibited macrophage M2 [43]
Caco-2; HT-29 in BALB/c nude mice expression polarization; prevented
colorectal liver metastasis
BMMSCs miR-16-5p Caco-2; SW480; Caco-2 BALB/c cell Downregulated ITGA2 Inhibited CRC cell [44]
SW620; LoVo; HT29 xenograft in BALB/c expression proliferation,
nude mice migration, and invasion
AMSCs - HCT-116 HCT-116 cell xenograft Upregulated TRPC3 Accelerated CRC progression [45]
in BALB/c nude mice expression by inducing the MT-CAF cell
phenotype
UCMSCs miR-431-5p Caco-2; SW480; SW620; LoVo cell xenograft in Downregulated PRDX1 Suppressed CRC cell growth [46]
LoVo; HCT 116 BALB/c nude mice expression
BMMSCs miR-4461 DLD1; HCT116; - Downregulated COPB2 Inhibited CRC cell [47]
SW480 expression tumorigenesis
Abbreviations: AMSCs: Adipose mesenchymal stem cells; BMMSCs: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; CAF: Cancer-associated fibroblasts;
MT: Mesenchymal stem cell-transformed; UCMSCs: Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells; MSC-exo: Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes;
CRC: Colorectal cancer; DLD: Deterministic lateral displacement.
PRDX1. Chen et al. demonstrated that miR-4461 level 3.4. Pancreatic cancer
47
46
is lower in CRC cells and tissues. BMMSC-exo-induced The prognosis for pancreatic cancer is extremely poor,
miR-4461 overexpression reduces CRC cell migration by characterized by difficulties in early diagnosis, low surgical
downregulating COPB2. Pishavar et al. developed an resection rates, and a high tendency for recurrence and
48
effective method to load SN38 into exosomes modified metastasis. Studies have indicated that the impact of MSC-
with MUC1 aptamers to target MUC1-overexpressing exo on pancreatic cancer varies and lacks consistency. Ding
cells, demonstrating good inhibitory effects on CRC. et al. discovered that miR-100-5p is highly expressed
51
In vivo studies in a BALB/c mouse C26 ectopic model in UCMSC-exo, promoting the growth of PANC-1 and
demonstrated that a single intravenous injection of BxPC3 cells. In addition, miR-145-5p is highly expressed
doxorubicin (DOX)-loaded MUC1-modified UCMSC- in UCMSC-exo, but it suppresses pancreatic ductal cell
exo (UCMSC-exo-DOX) significantly inhibited tumor carcinoma by inhibiting the TGF-β/Smad3 signaling
growth compared to the group with conventional DOX. pathway. Other studies have reported that BMMSC-
49
52
Additional research indicated that UCMSC-exo-DOX exo carrying miR-1231 can inhibit pancreatic cancer by
exhibited greater accumulation in tumors and quicker suppressing the EGFR/cyclin E pathway (Table 4).
53
clearance by the liver compared to the group treated with
conventional DOX. Han et al. constructed an iRGD- The TME of pancreatic cancer differs from that of other
50
Lysosome-associated membrane protein 2 (Lamp2b) tumors. Beyond the typical cellular elements, pancreatic
fusion gene-modified UCMSCs and isolated and purified cancer features an abundant extracellular matrix (ECM)
exosomes. They loaded anti-mir-221 into exosomes composed of collagen, matrix proteins, and a variety of
through electroporation. The findings demonstrated that soluble factors, including cytokines, chemokines, and
exosomes modified with iRGD effectively suppressed the growth factors. Essentially, the TME in pancreatic cancer
colony formation of CRC cells. It was further revealed is characterized by a dense stromal structure resulting
that these iRGD-modified exosomes were internalized by from excessive fibrosis driven by active connective tissue
CRC cells from their interaction with the NRP-1. In vivo proliferation and accumulation. This extensive fibrosis,
experiments also indicated a significant accumulation along with a lack of vasculature, immune infiltration, and
of iRGD-modified exosomes at the tumor site. Taken a hypoxic stromal environment, not only promotes tumor
50
together, MSC-exo holds great promise as drug delivery growth and invasion but also induces resistance to anti-
vehicles, but further research is warranted to fully realize tumor drugs. Therefore, studying the roles of different
the exosomes’ potential. components within the TME of pancreatic cancer and
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 6 doi: 10.36922/IMO025210025