Page 81 - IMO-2-3
P. 81
Innovative Medicines & Omics Synthesis and docking of diorganotin (IV) chelates
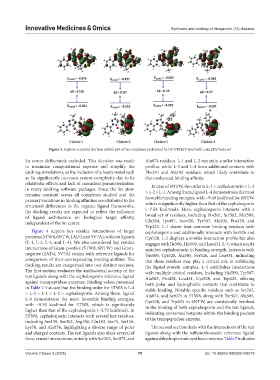
Figure 3. Highest occupied electron orbital plot of Sn-complexes performed by DFT/B3LYP level with LanL2DZ basis set
Sn center deliberately excluded. This decision was made Ala074 residues. L-1 and L-2 maintain similar interaction
to minimize computational expense and simplify the profiles, while L-3 and L-4 form additional contacts with
docking simulations, as the inclusion of a heavy metal such Phe241 and Ala182 residues, which likely contribute to
as Sn significantly increases system complexity due to its their enhanced binding affinity.
relativistic effects and lack of consistent parameterization In case of 6NTW, the order is L-4 > cephalosporin > L-3
in many docking software packages. Since the Sn atom > L-2 > L-1. Among them, ligand L-4 demonstrates the most
remains constant across all complexes studied and the
primary variations in binding affinities are attributed to the favorable binding energies, with −9.48 kcal/mol for 6NTW,
structural differences in the organic ligand frameworks, which is significantly higher than that of the cephalosporin
the docking results are expected to reflect the influence (−7.53 kcal/mol). Here, cephalosporin interacts with a
of ligand architecture on biological target affinity, broad set of residues, including Pro501, Ser502, Met500,
independent of the Sn center. Glu504, Lys497, Asn426, Tyr507, Ala505, Pro428, and
Trp425. L-1 shares four common binding residues with
Figure 4 depicts key residue interactions of target cephalosporin and additionally interacts with Ser526 and
proteins (5TW8, 6NTW, 1AD4, and 5V7A), with test ligands Cys528. L-2 displays a similar interaction profile but also
(L-1, L-2, L-3, and L-4). We also considered key residue engages with Ile506, His509, and Leu431. L-3, which nearly
interactions of Gram-positive (5TW8, 6NTW) and Gram- matches cephalosporin in binding strength, interacts with
negative (1AD4, 5V7A) strains with reference ligands for His509, Cys528, Ala505, Ser526, and Leu431, indicating
comparison of their corresponding binding abilities. The that these residues may play a critical role in stabilizing
docking results are categorized into two distinct sections. the ligand-protein complex. L-4 establishes interactions
The first section evaluates the antibacterial activity of the with multiple critical residues, including His509, Tyr507,
test ligands along with the cephalosporin reference ligand Ala505, Pro428, Leu431, Cys528, and Trp425, offering
against transpeptidase enzymes. Binding values presented both polar and hydrophobic contacts that contribute to
in Table 7 indicate that the binding order for 5TW8 is L-4 stable binding. Notably, specific residues such as Ser262,
> L-3 > L-1 > L-2 > cephalosporin. Among them, ligand Ala074, and Ser075 in 5TW8, along with Tyr507, Ala505,
L-4 demonstrates the most favorable binding energies, Cys528, and Trp425 in 6NTW, are consistently involved
with −8.50 kcal/mol for 5TW8, which is significantly in the binding of both cephalosporin and the test ligands,
higher than that of the cephalosporin (−5.72 kcal/mol). In indicating conserved hotspots within the binding pockets
5TW8, cephalosporin interacts with several key residues, of the transpeptidase enzyme.
including Ser139, Ser262, Arg186, Glu183, Ser75, Ser116,
Lys78, and Ala074, highlighting a diverse range of polar The second section deals with the interactions of the test
and charged contacts. The test ligands also share several of ligands along with the sulfamethoxazole reference ligand
these crucial interactions, notably with Ser262, Ser075, and against dihydropteroate synthase enzymes. Table 7 indicates
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 75 doi: 10.36922/IMO025140019