Page 67 - ITPS-7-1
P. 67
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Docking study of quinoline-3-carbaldehyde derives
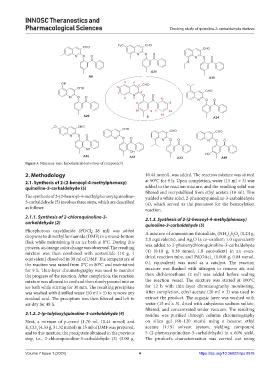
Figure 3. Nine non-toxic hypothetical derivatives of compound 5.
2. Methodology 10.44 mmol), was added. The reaction mixture was stirred
2.1. Synthesis of 2-(2-benzoyl-4-methylphenoxy) at 90°C for 9 h. Upon completion, water (15 ml × 3) was
quinoline-3-carbaldehyde (5) added to the reaction mixture, and the resulting solid was
filtered and recrystallized from ethyl acetate (10 ml). This
The synthesis of 2-(2-benzoyl-4-methylphenoxy)quinoline- yielded a white solid, 2-phenoxyquinoline-3-carbaldehyde
3-carbaldehyde (5) involves three steps, which are described (4), which served as the precursor for the benzoylation
as follows: reaction.
2.1.1. Synthesis of 2-chloroquinoline-3- 2.1.3. Synthesis of 2-(2-benzoyl-4-methylphenoxy)
carbaldehyde (2) quinoline-3-carbaldehyde (5)
Phosphorous oxychloride (POCl ; 28 ml) was added A mixture of ammonium thiosulfate, (NH ) S O (0.24 g,
3
dropwise to dimethylformamide (DMF) in a round-bottom 2.0 equivalents), and Ag O (a co-oxidant; 1.0 equivalent)
8
4 2 2
flask while maintaining it an ice bath at 0°C. During this was added to 2-phenoxychloroquinoline-3-carbaldehyde
2
process, an orange color change was observed. The resulting
mixture was then combined with acetanilide (10 g, 1 (4) (0.10 g, 0.38 mmol, 1.0 equivalent) in an oven-
equivalent) dissolved in 30 ml of DMF. The temperature of dried reaction tube, and Pd(OAc) (0.008 g, 0.04 mmol,
2
the reaction was raised from 0°C to 80°C and maintained 0.1 equivalent) was used as a catalyst. The reaction
for 9 h. Thin-layer chromatography was used to monitor mixture was flushed with nitrogen to remove air, and
the progress of the reaction. After completion, the reaction then dichloroethane (2 ml) was added before sealing
mixture was allowed to cool and then slowly poured into an the reaction vessel. The mixture was stirred at 100°C
ice bath while stirring for 30 min. The resulting precipitate for 12 h with thin-layer chromatography monitoring.
was washed with distilled water (50 ml × 5) to remove any After completion, ethyl acetate (20 ml × 3) was used to
residual acid. The precipitate was then filtered and left to extract the product. The organic layer was washed with
air-dry for 48 h. water (15 ml × 3), dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate,
filtered, and concentrated under vacuum. The resulting
2.1.2. 2-(p-tolyloxy)quinoline-3-carbaldehyde (4) residue was purified through column chromatography
Next, a mixture of p-cresol (1.70 ml, 10.44 mmol) and on silica gel (60–120 mesh) using a hexane: ethyl
K CO (4.33 g, 31.32 mmol) in 15 ml of DMF was prepared, acetate (1:19) solvent system, yielding compound
2
3
and to this mixture, the precipitate obtained in the previous 5 (2-phenoxyquinoline-3-carbaldehyde) in a 60% yield.
step, i.e., 2-chloroquinoline-3-carbaldehyde (2) (2.00 g, The product’s characterization was carried out using
Volume 7 Issue 1 (2024) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/itps.0976