Page 10 - ITPS-8-1
P. 10
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Image-assisted personalized interventions
PROCESS SCANNER
IMPLANT POSITION & DRUG SIZE
AFFECTED
AREA
POWER
POWER &
SOURCE CONTROL IMPLANT
HEALTHY TISSUES
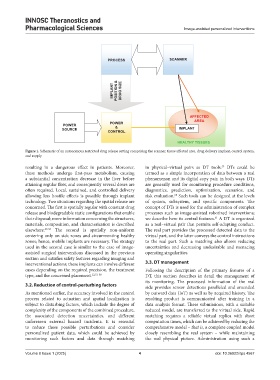
Figure 1. Schematic of an autonomous restricted drug release setting comprising the scanner, tissue affected area, drug delivery implant, control system,
and supply
resulting in a dangerous effect in patients. Moreover, in physical–virtual pairs as DT tools. DTs could be
59
these methods undergo first-pass metabolism, causing termed as a simple incorporation of data between a real
a substantial concentration decrease in the liver before phenomenon and its digital copy pair, in both ways. DTs
attaining regular flow, and consequently several doses are are generally used for monitoring procedure conditions,
often required. Local, sustained, and controlled delivery diagnostics, prediction, optimization, scenarios, and
allowing less hostile effects is possible through implant risk evaluation. Such tools can be designed at the levels
60
technology. Two situations regarding the spatial release are of system, subsystem, and specific components. The
concerned. The first is spatially regular with constant drug concept of DTs is used for the administration of complex
release and biodegradable static configurations that enable processes such as image-assisted robotized interventions;
their disposal; more information concerning the structures, we describe here its central features. A DT is organized
61
materials, composition, and characterization is described as a real–virtual pair that permits self-adapting conduct.
elsewhere. 40-50 The second is spatially non-uniform The real part provides the processed detected data to the
centering only on sick zones and circumventing healthy virtual part, and the latter conveys the control instructions
zones; hence, mobile implants are necessary. The strategy to the real part. Such a matching also allows reducing
used in the second case is similar to the case of image- uncertainties and decreasing undesirable and menacing
assisted surgical interventions discussed in the previous operating singularities.
section and satisfies safety features regarding imaging and
interventional actions; these implants can involve different 3.3. DT management
cases depending on the required precision, the treatment Following the description of the primary features of a
type, and the concerned placement. 12,51-58 DT, this section describes in detail the management of
its monitoring. The processed information of the real
3.2. Reduction of control-perturbing factors side provides sensor detections paralleled and amended
As mentioned earlier, the accuracy involved in the control by outward data (IoT) as well as by acquired history. The
process related to actuation and spatial localization is resulting product is communicated after training in a
subject to disturbing factors, which include the degree of data analysis format. These submissions, with a suitable
complexity of the components of the combined procedure, reduced model, are transferred to the virtual side. Rapid
the associated detection uncertainties, and different matching requires a reliable virtual replica with short
unforeseen external hazard incidents. It is essential computation times, which can be achieved by reducing the
to reduce these possible perturbations and consider comprehensive model – that is, a complete coupled model
personalized patient data, which could be achieved by closely resembling the real system – while maintaining
monitoring such factors and data through matching the real physical picture. Administration using such a
Volume 8 Issue 1 (2025) 4 doi: 10.36922/itps.4567